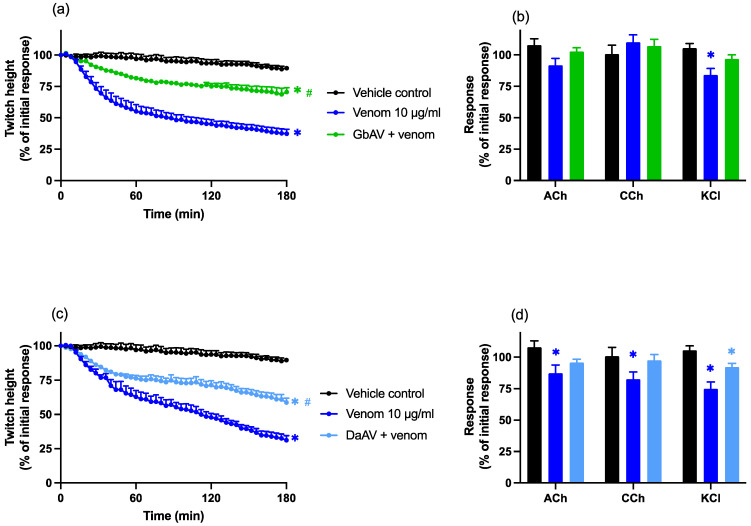
Figure 7.
Effects of (a,b) Chinese G. brevicaudus monovalent antivenom (GbAV; 150 µL; 2× the recommended concentration) or (c,d) Chinese D. acutus antivenom (DaAV; 35 µL; 3× the recommended concentration) in the chick biventer cervicis nerve–muscle preparation. Effects of venom, in the presence and absence of Chinese GbAV, on (a) indirect twitches and (b) contractile responses to exogenous agonists; ACh (1 mM), CCh (20 µM), and KCl (40 mM). Effects of venom, in the presence and absence of Chinese DaAV, on (c) indirect twitches and (d) contractile responses to exogenous agonists; ACh (1 mM), CCh (20 µM), and KCl (40 mM). (a,c) * p < 0.05, significantly different to the vehicle control; # p < 0.05, significantly different to venom in the absence of antivenom, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. (b,d) * p < 0.05, significantly different to pre-venom response, paired t-test; # p < 0.05, significantly different to venom in the absence of antivenom, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. N = 5–6, where n is the number of preparations from different animals.