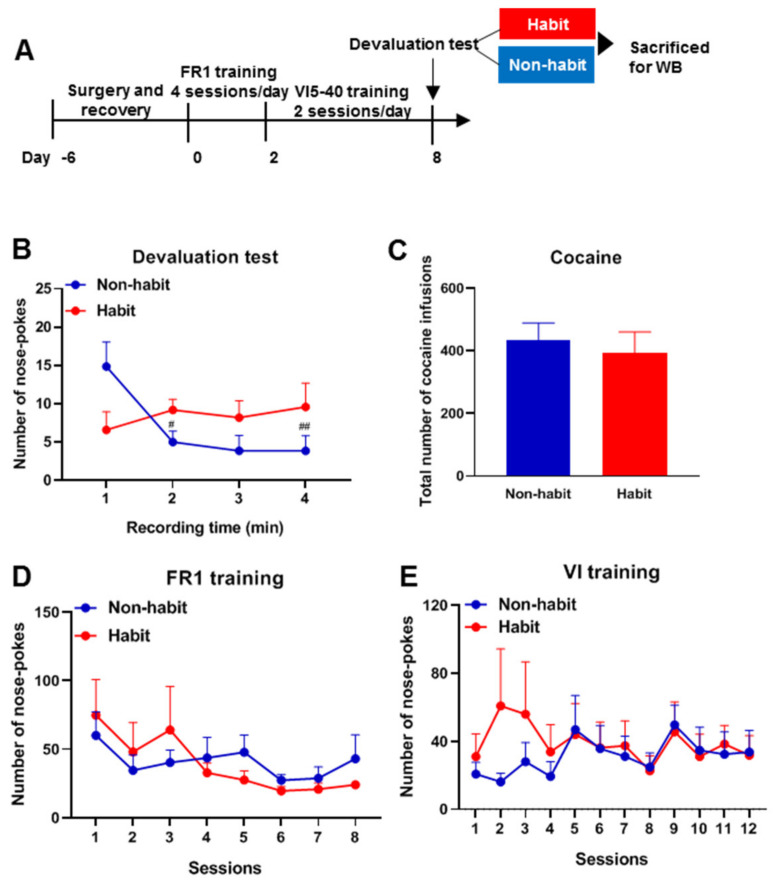
Figure 1.
The establishment of habitual cocaine-seeking behavior in tree shrews. (A) The protocol for the training of cocaine habitual behavior. (B) In the devaluation test after variable interval (VI) training, the habit group exhibited a slightly increase nose pokes during each 10-min interval compared with the first 10 min, which is also not high enough to be statistically significant, but the non-habit group exhibited a decreased number of nose pokes in the periods of 10–20, 20–30, and 30–40 min compared with the period of 0–10 min. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, the number of valid nose pokes in the non-habit group compared with the number of valid nose pokes in the first 10 min. (C) The received dose of cocaine was no different between the non-habit tree shrews and the habit tree shrews. (D) The number of valid nose pokes in the FR1 training was no different between the two groups. (E) The number of valid nose pokes in the VI training was no different between the two groups. The data were expressed as the means ± SEM and analyzed with a two-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test or the t-test, habit group n = 5, non-habit group n = 7.