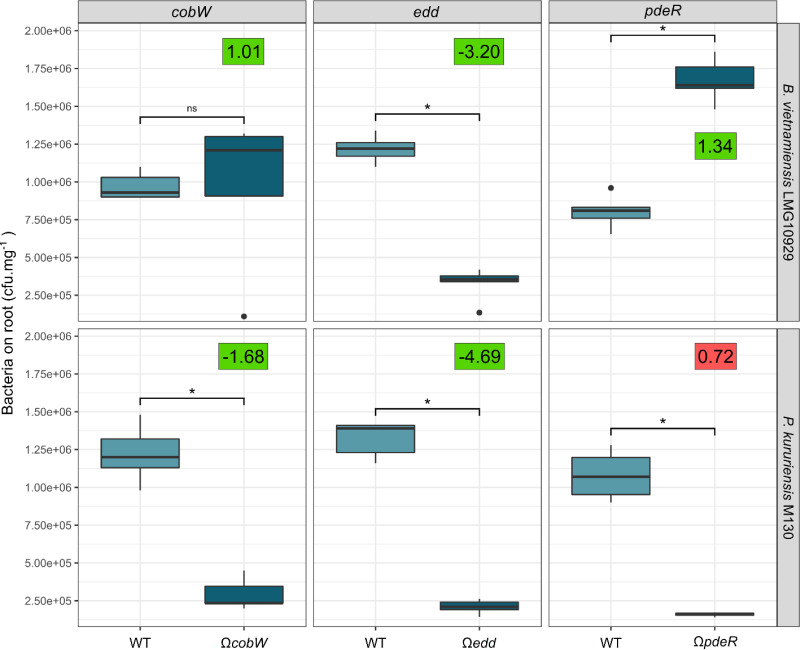
FIG 6.
Colonization capacity of B. vietnamiensis and P. kururiensis insertion mutants in competition assays. Three genes, cobW, edd, and pdeR, predicted by the Tn-seq approach to be involved in rice root colonization were selected for targeted disruption in B. vietnamiensis and P. kururiensis. Mutants and WT strains were inoculated simultaneously on Nipponbare rice roots and enumerated at 7 dpi. Significance levels of pairwise comparisons were estimated using a Wilcoxon test (P < 0.05). For each mutant, the log2 fold change (FC) value observed in the Tn-seq on Nipponbare is displayed. Positive and negative correlations with the mutagenesis approach are expressed with green and red squares, respectively.