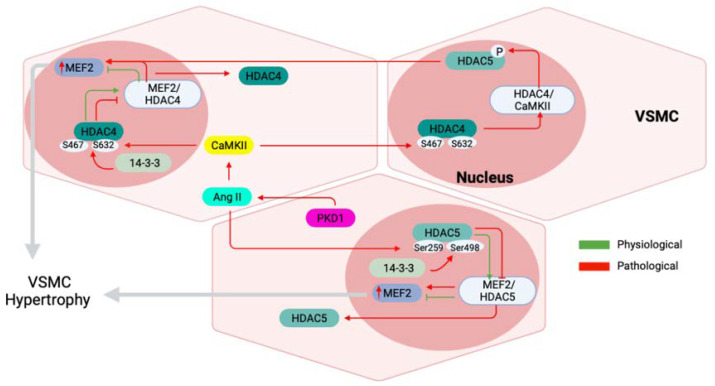
Figure 3.
Pathological mechanisms of VSMC hypertrophy. Angiotensin II (AngII) leads to phosphorylation of HDAC4/5 chaperone 14-3-3 binding sites through CaMKII-dependent (HDAC4) and CaMKII-independent (HDAC5) mechanisms. Under physiological conditions, HDAC4/5 forms complexes with myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2). Under pathological conditions, complex formation is downregulated and MEF2 leads to activation of hypertrophic genes for contractile proteins such as beta-MHC, atrial natriuretic factor (ANF), and transcription factor KLF5, leading to VSMC hypertrophy.