Figure 1.
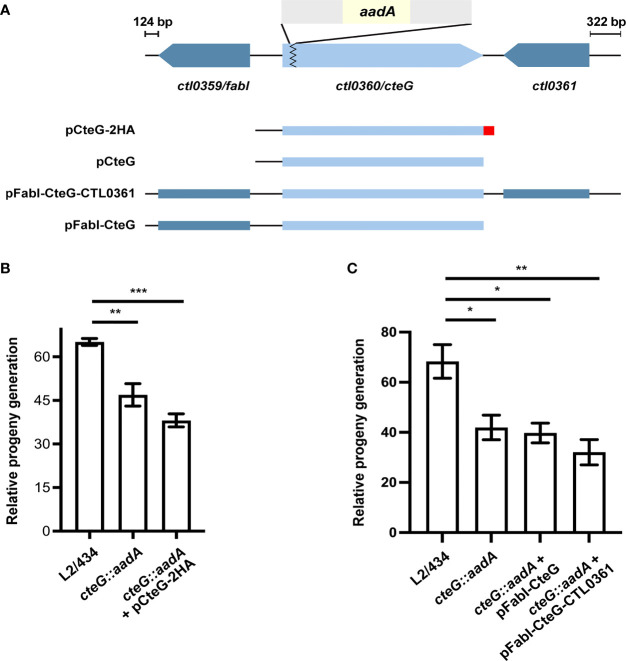
A C. trachomatis cteG::aadA insertional mutant is defective in progeny generation. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic region of ctl0360/cteG (light blue), which was disrupted by insertion of a modified group II intron (grey) carrying a spectinomycin-resistance gene, aadA (yellow) to generate a C. trachomatis cteG mutant strain (cteG::aadA) (Pais et al., 2019). The cteG::aadA mutant strain was transformed with plasmids encoding CteG fused to a double hemagglutinin tag (2HA; red; pCteG-2HA; also named pCteG-2HA[Pgp4+] in Table 1 and in Figures 4 , 5 ), native CteG (pCteG) ( Supplementary Figure S1 ), or CteG and two (ctl0359/fabI and ctl0361; pFabI-CteG-CTL0361) or one (ctl0359/fabI; pFabI-CteG) of its flanking genes (dark blue). (B) Two identical tissue culture plates seeded with HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis L2/434, cteG::aadA mutant and complemented (cteG::aadA harboring a plasmid encoding CteG-2HA, also named pCteG-2HA[Pgp4+] in Table 1 and in Figures 4 , 5 ) strains at a MOI of 0.06. In one plate (input), the IFUs obtained in a primary infection were quantified at 24 h p.i. by immunofluorescence microscopy after fixation and immunolabelling of the chlamydiae; in the second plate (output), cells were lysed at 40 h p.i. and the number of released infectious particles were quantified after infecting for 24 h a new plate seeded with HeLa cells followed by fixation, immunolabelling of the chlamydiae, and immunofluorescence microscopy. For each strain, the relative progeny generation was obtained by dividing the number of IFUs in the output by those in the input. See Materials and Methods for a detailed description of the procedure. (C) cteG::aadA mutant strains harboring pFabI-CteG or pFabI-CteG-CTL0361 (see Panel A) were assessed in terms of infectious progeny generation as in (B) by comparison with the parental (L2/434) and mutant (cteG::aadA) strains. Data in (B, C) correspond to the mean ± standard error of the mean (n=3). Statistical significance was determined by using ordinary one-way ANOVA and Dunnett post-test analysis relative to the L2/434 strain (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001).