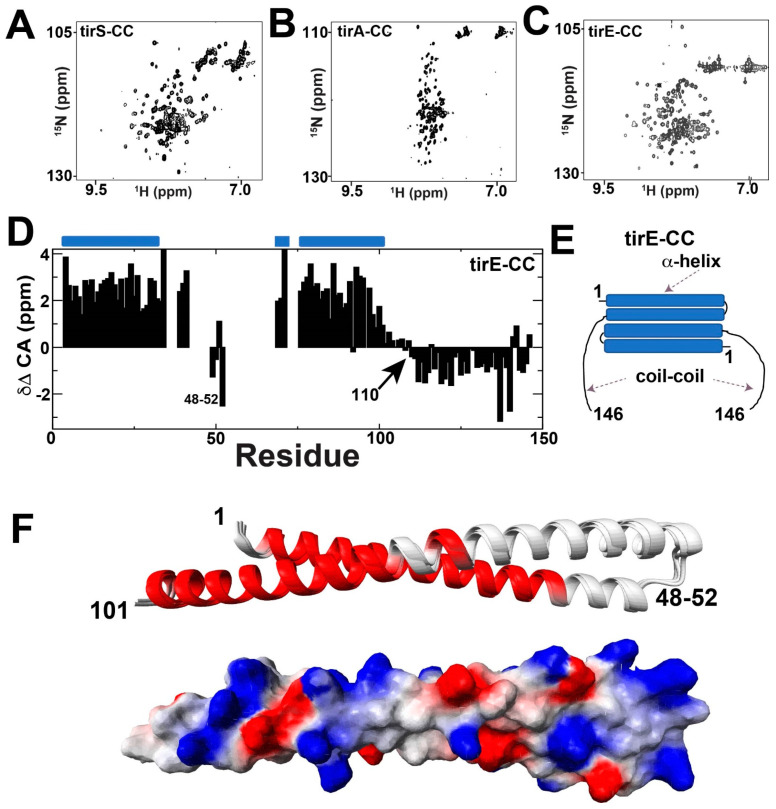
Figure 4.
NMR studies of TIR-containing CC domains. (A) tirS CC in 50 mM Na2HPO4, 500 mM NaCl, pH 6.5. (B) tirA CC in 50 mM Na2HPO4, 50 mM NaCl, pH 6.5. (C) tirE CC in 50 mM Na2HPO4, 150 mM NaCl, pH 6.5. (D) CA chemical shift propensities (δΔ CA) of tirE-CC were calculated by the CA chemical shift for each residue type and subtracting random coil CA resonance reported for that same residue type at the BMRB (http://www.bmrb.wisc.edu/, accessed on 30 May 2022). Secondary structure predictions of helices (blue barrel) are shown, as predicted by CSI version 2.0 [36]. (E) Proposed secondary structure based on the chemical shift propensities of tirE-CC. (F) Top five structures determined from CS-Rosetta with α-helices predicted from experimental chemical shifts (red) and electrostatic surface representation (red is negative charge, blue is positive charge), shown below as calculated in Molmol [37].