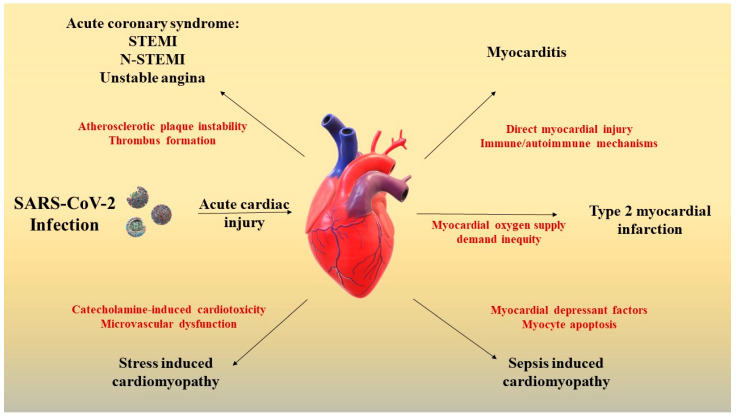
Figure 1.
Potential pathophysiological mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 induced acute cardiac injury; acute coronary syndromes occur by destabilization and rupture of atheroma plaques with the consequent formation of a thrombus that causes occlusion of the artery responsible for heart attack [41]. Myocarditis can occur through direct myocardial injury and immune or autoimmune mechanisms [72,73,74]. Type 2 myocardial infarction occurs due to an imbalance between the need and supply of oxygen [12]. Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy occurs due to myocytic apoptosis and cardiodepressant factors [82,83]. Stress-induced cardiomyopathy occurs through the cardiotoxic effect of catecholamines and is secondary to microvascular dysfunction [85]. Legend: STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; and N-STEMI: non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction.