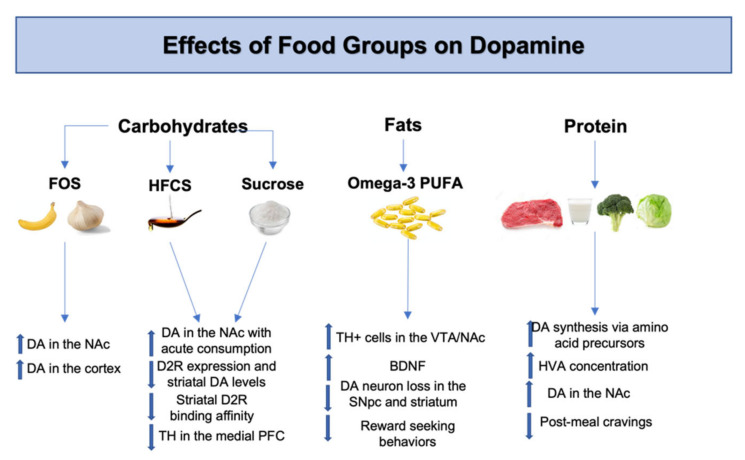
Figure 2.
Effects of food groups on dopamine. FOS consumption increases dopamine levels in the NAc and the cortex [46,47]. Acute HFCS and sucrose consumption increases dopamine in the NAc [48]. Chronic HFCS and sucrose consumption decreases D2R expression, D2R binding affinity, striatal dopamine levels and TH in the medial PFC [50,52]. Omega-3 PUFA increase BDNF and TH+ cells in the VTA and NAc [57]. Omega-3 PUFA decrease dopamine neuron loss in the SNpc and striatum [58], while also reducing reward seeking behavior [59]. Protein intake increases dopamine synthesis, dopamine levels in the NAc and HVA concentrations while decreasing post-meal cravings [60,61,62]. Abbreviations: FOS, fructo-oligosaccharides; HFCS, high-fructose corn syrup; PUFA, poly-unsaturated fatty acids, DA, dopamine; NAc, nucleus accumbens; D2R, dopamine 2 receptor; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; PFC, pre-frontal cortex; BDNF, brain derived neurotrophic factor; VTA, ventral tegmental area; SNpc, substantia nigra pars compacta; HVA, homovanillic acid.