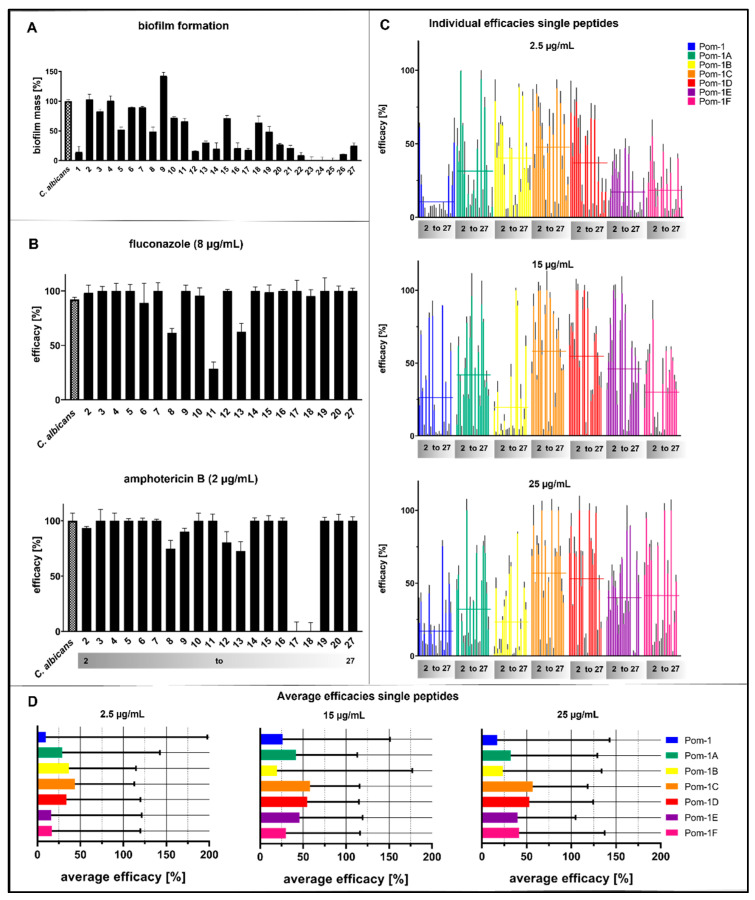
Figure 3.
Detection of the biomass and antifungal activity of Pom-1 derivatives towards biofilm formation of invasive C. albicans clinical isolates by crystal violet assay. All the experiments were performed in triplicate, and the error bars depict the standard deviations. (A) Biofilm formation of Candida isolates without an agent. A laboratory strain of C. albicans was used as a reference. The Candida isolates were named with numbers. (B) Effect of fluconazole and amphotericin B on biofilm formation of the clinical isolates. The maximum inhibitory concentrations of 8 µg/mL for fluconazole and 2 µg/mL for amphotericin B were used. The Candida isolates were named with numbers. The grey bar was added to indicate the isolates to allow more transparency in the following figures (2–27). (C) Evaluated effects of 2.5 µg/mL (MIC), 15 µg/mL, and 25 µg/mL Pom-1A to Pom-1F on the biofilm mass of the clinical isolates. Each bar represents one isolate, repeated for each derivative. The mean values of the corresponding peptides are illustrated with horizontal lines. The evaluation of the individual peptides is continuously indicated with a grey color gradient. Pom-1 was tested as a control agent. A laboratory strain of C. albicans was used as a reference. (D) Summary of the average efficacies of Pom-1 and its derivatives based on (C). The average efficacies correspond to the mean values.