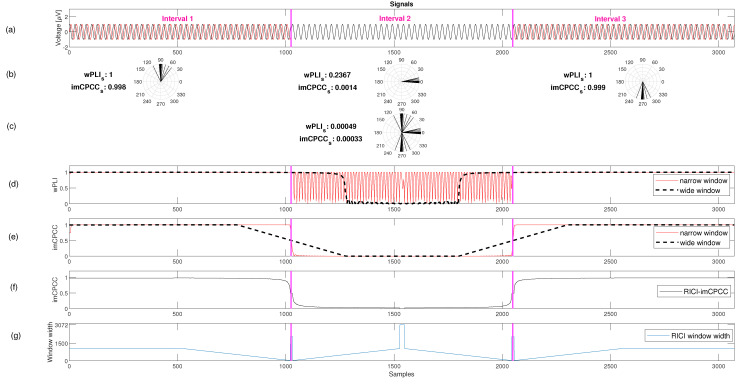
Figure 6.
An example of a RICI-imCPCC estimation procedure for the ideal synthetic signals ( [37]. For an example, the confidence interval was obtained for [38,39]). (a) Two synthetic sinusoidal signals considered as a pair of electrode signals. The phase angle difference between these signals is different in three intervals separated by magenta vertical lines. (b) The calculated temporal functional connectivity of wPLI and imCPCC for each of the intervals separately with predefined interval boundaries. In addition, this line shows the distribution of the unit vector phase angle differences in the polar domain. (c) This gives us an insight into the static functional connectivity imCPCC value calculated for the entire signal period and the distribution of unit vector phase angle differences in the polar domain. (d,e) The estimated wPLI and imCPCC values calculated using the sliding constant window analysis method with narrow (window size equal to 10 samples) and wide (window size equal to 500 samples) windows. (f) The estimate using the RICI-imCPCC method, and (g) the change in window width for each observed sample defined using the RICI-imCPCC method.