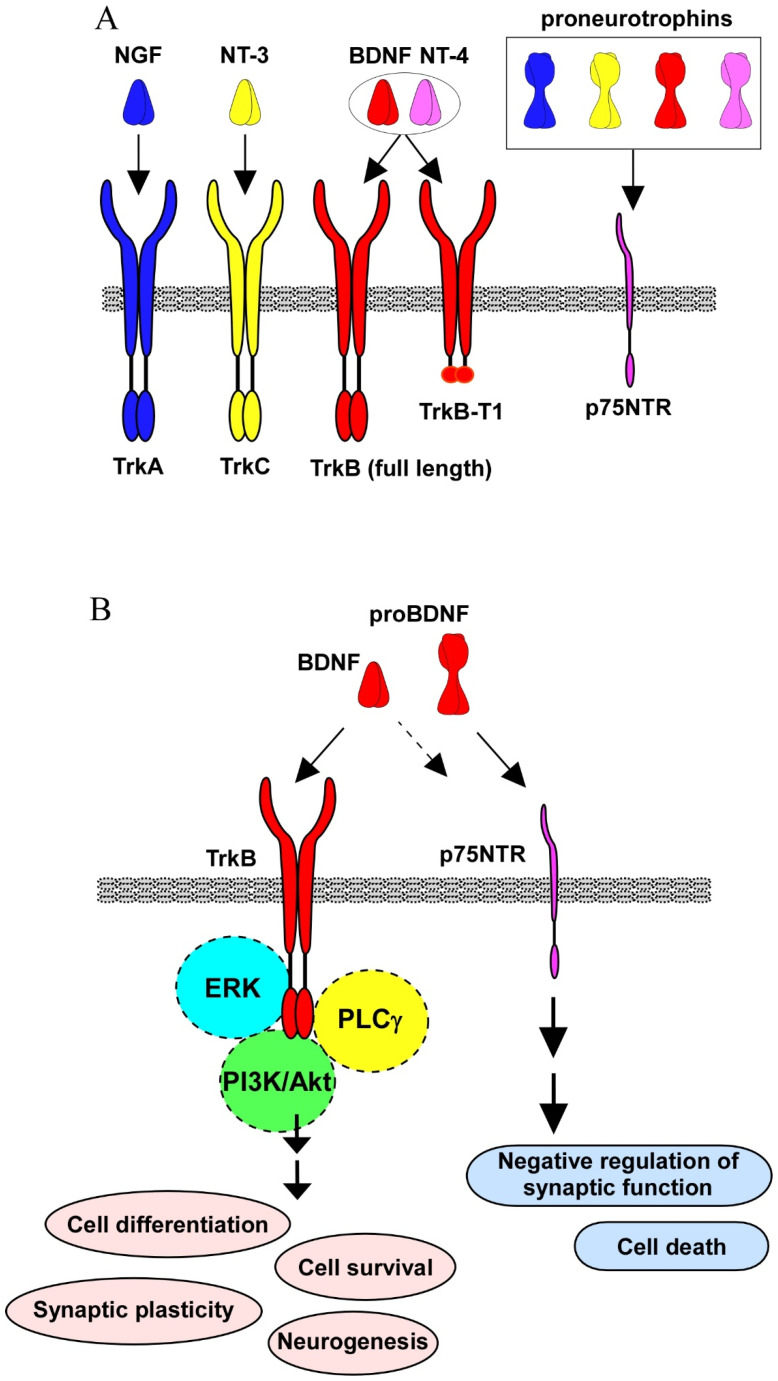
Figure 1.
Neurotrophins, receptors, and intracellular signaling. (A) Neurotrophins consist of nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4 (NT-4). Each neurotrophin has high affinity receptor; NGF binds to TrkA, BDNF and NT-4 to TrkB, and NT-3 to TrkC. In addition, all neurotrophins bind to p75NTR with low affinity. Mature (processed) neurotrophin is firstly translated as a precursor proneurotrophin which has high affinity for p75NTR. (B) Activation of TrkB stimulated by BDNF triggers downstream intracellular signaling pathways (mainly, PI3K/Akt, ERK, and phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) contributes to positive regulation of cell differentiation, survival, synaptic function, and neurogenesis. p75NTR-mediated signaling is involved in negative regulation of cell survival and synaptic function. Truncated isoform TrkB.T1 exerts a dominant-negative role against the function of full-length TrkB or a BDNF scavenging effect in the CNS.