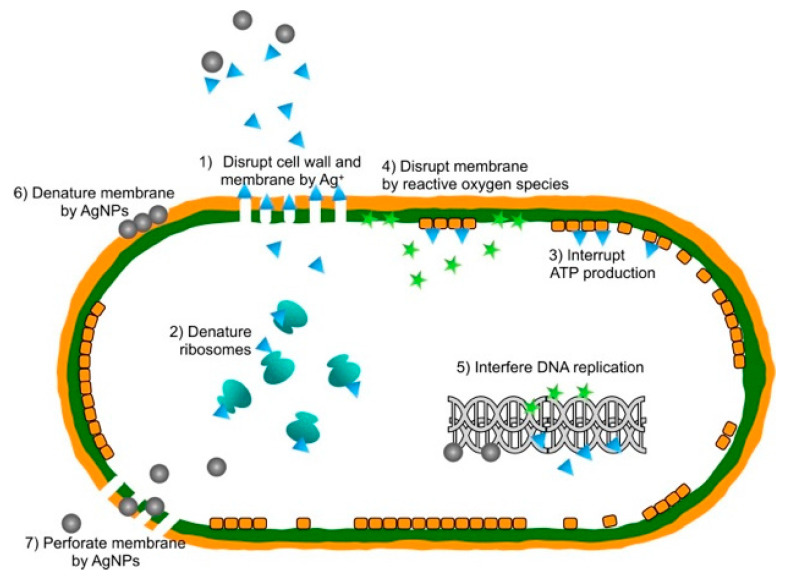
Figure 1.
The antibacterial actions of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). (1) Disruption of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane: silver ions (Ag+) released from silver nanoparticles adhere to or pass through the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane. (2) Denaturation of ribosomes: silver ions denature ribosomes and inhibit protein synthesis. (3) Interruption of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production is terminated because silver ions deactivate respiratory enzymes on the cytoplasmic membrane. (4) Membrane disruption by reactive oxygen species: reactive oxygen species produced by the broken electron transport chain can cause membrane disruption. (5) Interference of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication: silver and reactive oxygen species bind to deoxyribonucleic acid and prevent replication and cell multiplication. (6) Denaturation of membrane: silver nanoparticles accumulate in the cell wall pits and cause membrane denaturation. (7) Perforation of membrane: silver nanoparticles directly move across the cytoplasmic membrane, which can release organelles from the cell. Reprinted with permission from [14]. Originally published by and used with permission from Dove Medical Press Ltd. Copyright remains with the author and Dove Medical Press Limited, no transfer of copyright is inferred or implied.