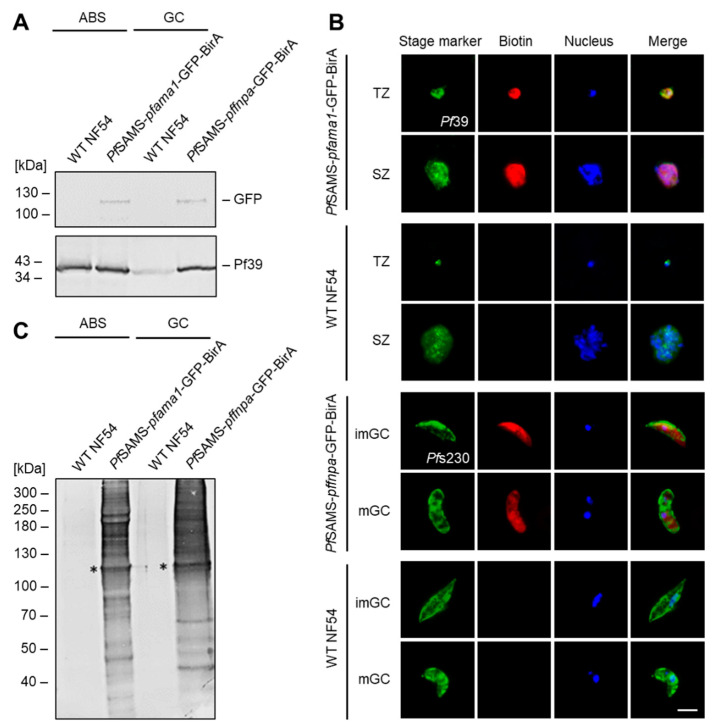
Figure 4.
Generation and verification of PfSAMS-GFP-BirA parasite lines. (A) Verification of PfSAMS expression. Lysates of asexual blood stages (ABS) of the PfSAMS-pfama1-GFP-BirA and gametocytes (GC) of the PfSAMS-pffnpa-GFP BirA lines were subjected to Western blotting to detect PfSAMS-GFP-BirA (108 kDa), using mouse anti-GFP antibody. Immunoblotting with rabbit antisera directed against Pf39 (39 kDa) served as a loading control. WT NF54 lysates were used as negative controls. (B) Localization of biotinylated proteins in the PfSAMS-GFP-BirA blood stages. Asexual blood stages of the PfSAMS-pfama1-GFP-BirA line and gametocytes of the PfSAMS-pffnpa-GFP-BirA line were treated with 50 μM biotin for 24 h. WT NF54 was used as a negative control. Immunofluorescence assays were employed, using mouse antibodies directed against Pf39 to highlight trophozoites (TZ), and schizonts (SZ) and rabbit antisera directed against Pfs230 to highlight immature (imGC) and mature (mGC) gametocytes (green). Biotinylated proteins were immunolabeled using fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (red). The nuclei were labeled with Hoechst 33342 nuclear stain (blue). Bar; 5 µm. (C) Detection of biotinylated proteins in the PfSAMS-GFP-BirA lines. Lysates of asexual blood stages (ABS) from the PfSAMS-pfama1-GFP-BirA line and gametocytes (GC) of the PfSAMS-pffnpa-GFP-BirA line were produced following treatment of the cultures with 50 μM biotin for 24 h. Streptavidin coupled to alkaline phosphatase was used for immunoblotting. Asterisks indicate the expected band for PfSAMS-GFP-BirA (~108 kDa). The results are representative of two (A,C) or three (B) independent experiments.