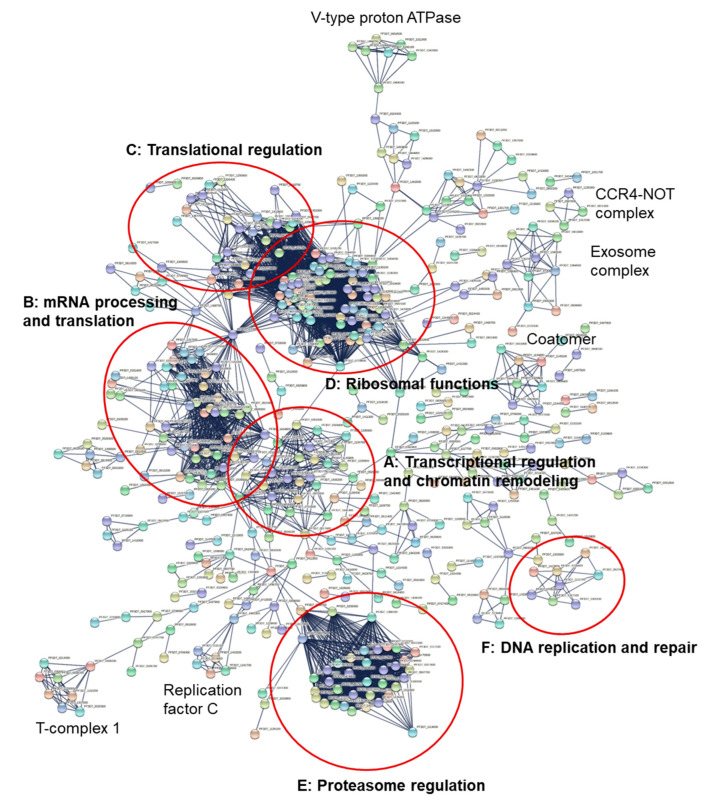
Figure 6.
Network analysis of the putative interactors of PfSAMS. A list of 1114 query proteins was evaluated for potential interactions using the String database. A network of potential PfSAMS interactors was predicted with a confidence level of 0.009. A Markov Clustering (MCL) algorithm was used to describe possible clusters with an inflation parameter of 3. Based on the physical interaction among only the query proteins, different clusters were identified built on the first shell of interaction with the following functions: (A) transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling with at least 20 member proteins; (B) mRNA processing and translation, including proteins of the spliceosome comprised of a subnetwork of more than 29 proteins, in contact with cluster A (C) Translational regulation with a cluster of translation regulation factors, that include mainly eukaryotic translation initiation factors; (D) ribosomal functions with ribosomal proteins presenting the largest cluster of the network, in contact with cluster C (E) proteasome regulation with a cluster of proteasome subunits with at least 38 connected proteins; (F) DNA replication and repair in a subnetwork of mainly mini-chromosome maintenance (MCM) proteins and DNA helicases, with no clear link to the other clusters. Smaller clusters of distinct protein complexes are indicated. Detailed information about individual proteins clustering in each subnetwork is provided in Table S4.