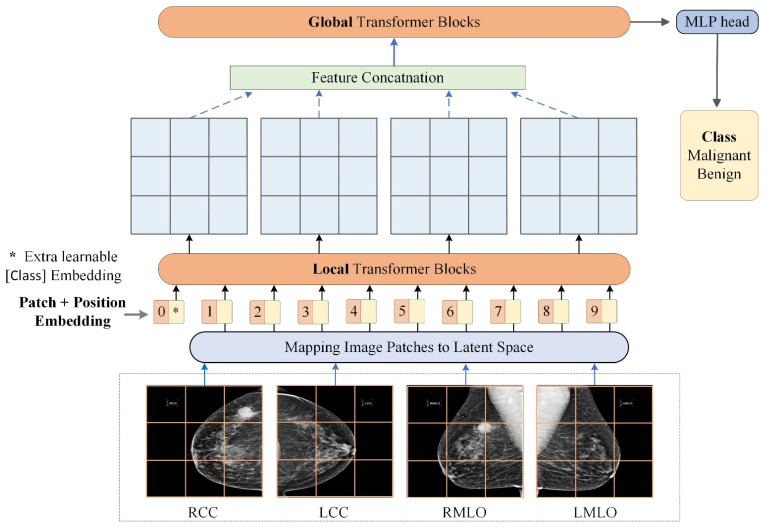
Figure 1.
Overview of using transformers for multi-view mammogram analysis. For a patient, each of the LCC, RCC, LMLO, and RMLO mammogram is split into image patches and mapped to embedding vectors in the latent space. Then, positional embeddings are added to patch embeddings. The sequence of embedding vectors is sent into local transformer blocks to learn within-mammogram dependencies. Weights of local transformer blocks are shared among the four mammograms. The four outputs are concatenated into one sequence and fed into global transformer blocks to learn inter-mammogram dependencies. The class token of the last global transformer block is sent into an MLP head to classify the case as benign/malignant.