Fig. 3.
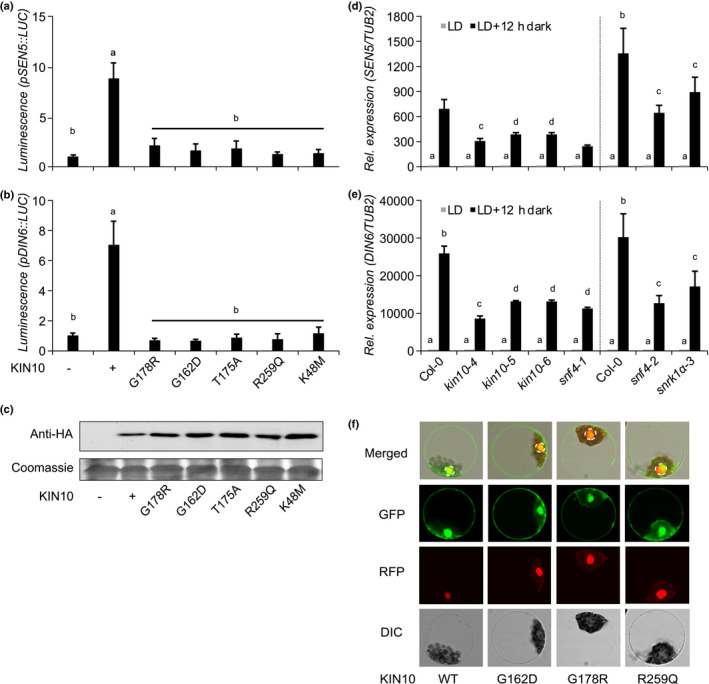
Mutations identified in Arabidopsis KIN10 and SNF4 result in nonfunctional KIN10 kinase. (a, b) SEN5 (a) and DIN6 (b) promoter activity in Arabidopsis thaliana leaf protoplasts upon transient expression of wild‐type and mutant KIN10 protein versions 6 h after transfection. G178R (kin10‐4), G162D (kin10‐5), R259Q (kin10‐6), K48M (KIN10 catalytic domain) and T175A (KIN10 T‐loop). Values are averages with standard deviations (n = 4). ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was applied, letters represent the statistical differences (P < 0.001) and error bars represent SD. (c) Protein expression was assessed by immunoblot analysis with anti‐HA antibodies. Coomassie staining of Rubisco small subunit (RBCS) served as a loading control. (d, e) SEN5 (d) and DIN6 (e) endogenous expression in 14‐d‐old single kin10 and snf4 mutants. LD, long days. Vertical dashed black lines separate the RT‐qPCR results of two independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD of three biological replicates. ANOVA Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was applied and letters represent the statistical differences among genotypes (P < 0.001). (f) Subcellular localization of GFP‐tagged KIN10 proteins in A. thaliana leaf mesophyll protoplasts. An SCF30‐RFP nuclear marker was coexpressed. Dashed circles indicate the nucleus. DIC, differential interference contrast.
