FIGURE 1.
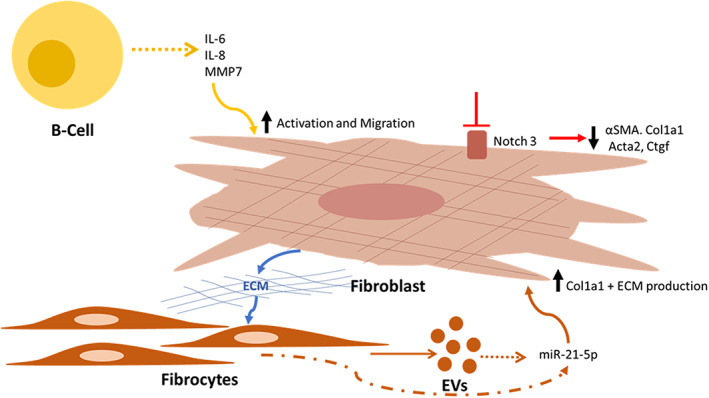
Recently reported pathogenic mechanisms in interstitial lung disease. B cells secrete profibrotic and pro‐inflammatory proteins in response to microbial antigens, and increased IL‐6, IL‐8 and matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) lead to activated fibroblasts and increased migration. 16 The Notch pathway is involved in myofibroblast differentiation, and reduced Notch3 signalling results in less α‐smooth muscle actin (αSMA), collagen type 1 (Col1a1) and other profibrotic gene expression from fibroblasts. 17 Abnormal extracellular matrix (ECM) in fibrotic lung tissue increases the expression of cellular and extracellular vesicle (EV) expressed miR‐21‐5p from fibrocytes, which exert pro‐fibrotic effects and upregulation of Col1a1 in fibroblasts leading to further ECM 19
