FIGURE 3.
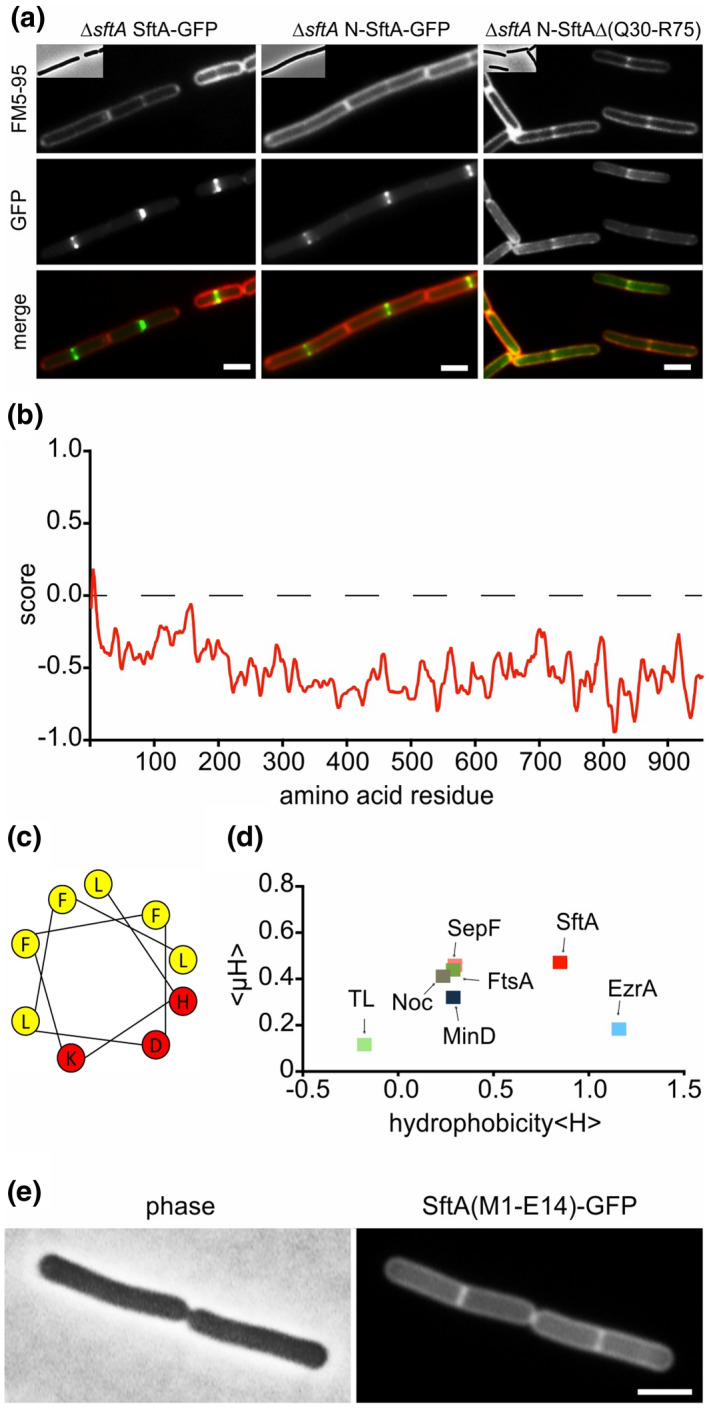
Membrane targeting of SftA. (a) Microscopic images of cells expressing SftA‐GFP, a deletion variant expressing only the N‐terminal 149 amino acids of SftA (N‐SftA‐GFP), and the same fusion construct lacking amino acids Q30 to R75. Membranes were stained with FM5‐95. (b) Amphipaseek plot (Sapay et al., 2006) indicates a possible amphipathic alpha‐helix at the extreme N‐terminus of SftA. (c) Helical wheel projection of this N‐terminal amphipathic helix (amino acids 4–12) with hydrophobic (yellow) and polar (red) amino acids. (d) Hydrophobicity (<H>) of different amphipathic helices plotted against their mean amphipathic moment (<μH>). See main text for details on the different helices. TL = thermolysin. (e) Localization of GFP fused to the N‐terminal amphipathic helix of SftA (amino acids M1‐E14). Expression of GFP fusions was induced with 0.1% xylose. Scale bars are 2 μm. Strains used: (a) TNVS455, TNVS456, TNVS234, and (e) TNV586, respectively
