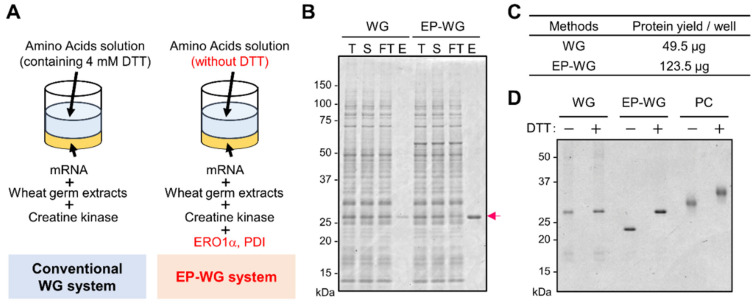
Figure 1.
Production of SARS-CoV-2 RBD containing disulfide bonds using the wheat germ cell-free protein synthesis system. (A) Schematic diagram of the different wheat germ (WG) cell-free protein synthesis methods. DTT-free amino acid substrate solution and WG containing ERO1α and PDI (EP-WG) was used for the synthesis of disulfide-bond-intact protein. (B) Purification of RBD using nickel-chelated sepharose beads. Each protein fraction was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by CBB staining. Arrow indicates the RBD. T, Total; S, Supernatant; FT, Flow Through; E, Elution. (C) Comparison of protein yield synthesized by two methods. Protein yield was normalized by expression scale (1 well of 6-multi-well plate). Protein concentrations of purified protein were quantified by bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. (D) Confirmation of disulfide bond formation of RBD using non-reducing SDS-PAGE analysis. Each protein was incubated with or without 100 mM of DTT for 30 min at 37 °C prior to SDS-PAGE analysis. Commercially available RBD protein produced by mammalian cell expression system was used as positive control (PC).