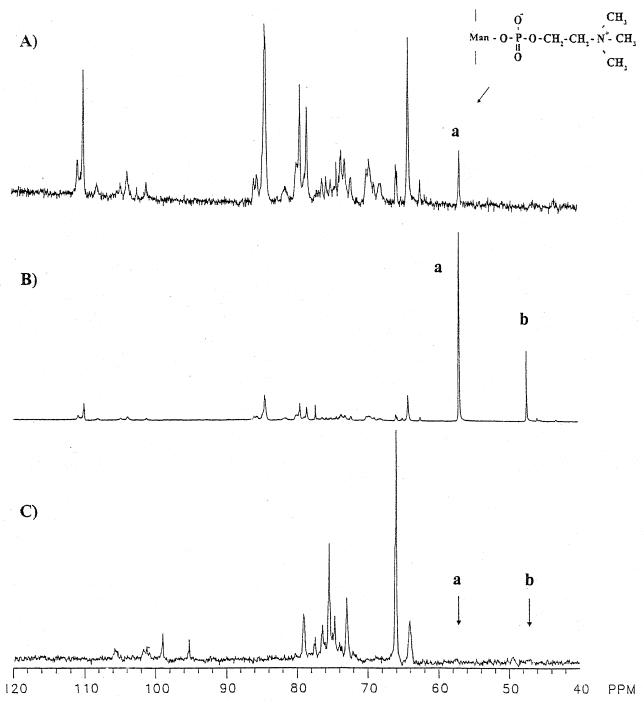
FIG. 3.
Effect of phosphate concentration on the release of galactofuranosyl residues from pPxGMii. Proton-decoupled 13C NMR spectra of extracellular pPxGMii isolated from day 8 culture filtrates are shown. (A) Spectrum of pPxGMii obtained from a culture originally in 20 mM phosphate medium [methyl- 13C]phosphocholine-containing pPxGMii (200 mg per 200 ml of medium) was added on day 3 to separate cultures originally in 20 mM and 2 mM phosphate. (B and C) Spectra of pPxGMii from cultures in 20 mM phosphate and 2 mM phosphates, respectively. Spectra of pPxGMii were recorded with 13,476, 18,557, and 13,649 acquisitions for panels A, B, and C, respectively. Ninety-degree radiofrequency pulses of 25 μs were applied at 4-s intervals. The signal designated “a” at 56.75 ppm is of the methyl carbons of phosphocholine attached to C-6 of mannopyranosyl residues in pPxGMii. The signals at 110.6, 109.6, 84.0, and 80.1 are those of the nonreducing terminal C-1 and internal C-1, C-2 and C-4, and C-5 atoms of 5-O-β-d-galactofuranosyl residues, respectively, of pPxGMii. The signals are as assigned by Unkefer et al. (40, 42). (Reprinted from reference 29 with permission from the publisher.)