Fig. 3.
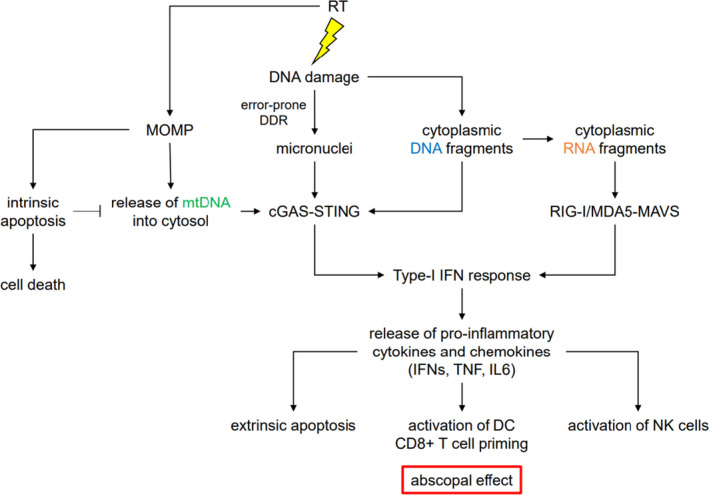
RT induces MOMP, which triggers activation of Caspase 9‐mediated intrinsic apoptosis. If the intrinsic apoptosis is inhibited, MOMP results in release of mtDNA into a cytosol. RT also directly damages DNA leading to accumulation of cytoplasmic DNA fragments. Moreover, incorrect damage repair, drives the formation of micronuclei. mtDNA, cytoplasmic DNA and micronuclei are recognized by cGAS, which stimulates production of type‐1 IFNs in a STING‐IRF3‐dependent manner. Additionally, cytoplasmic DNA fragments can be transcribed into RNAs by the RNA polymerase III. Through activation of RIG‐I/MDA5‐MAVS‐IRF3 pathway cytoplasmic RNA species can also promote IFN‐1 signalling. Subsequent release of pro‐inflammatory cytokines and chemokines triggers Caspase 8‐mediated extrinsic apoptosis, and anti‐tumour immunity by CD8+ T and NK cells. Importantly, the anti‐tumour immunity is directed against distal lesions as well as the irradiated site in a process called the abscopal effect. RT, radiotherapy; MOMP, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; cGAS, cyclic GMP–AMP synthase; IFN, interferon; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; IRF3, interferon regulatory factor 3; RIG‐I/MDA5‐MAVS, retinoic acid‐inducible gene I/melanoma differentiation‐associated gene 5‐mitochondrial antiviral‐signalling protein. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
