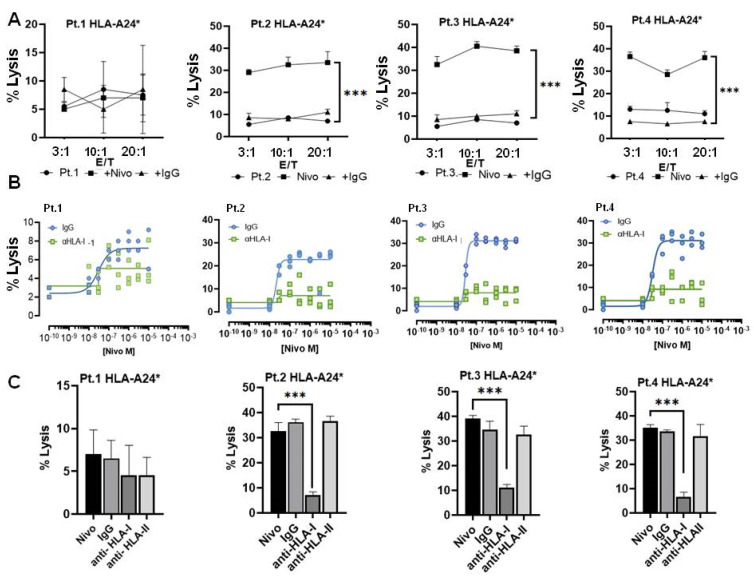
Figure 5.
(A) Cytotoxicity assay of autologous CD8+ T cells stimulated with CD3/CD8 antibodies for 24 h. Stimulated CD8 T cells were then tested for their cytotoxicity toward HLA-A24* autologous sarcoma tumor cells using different effector/target cell ratios (E/T) in four patients (Pt.1, Pt.2, Pt.3 and Pt.4) with different histology (see legend of Figure 4A). Nivolumab or IgG1 isotype antibodies at 1 µg/mL were added as adjuvant effector or control. Following incubation for 24 h, cytotoxicity was measured using a CytoTox-Fluor™ Cytotoxicity kit (Promega, G9261). (B) Dose response to Nivolumab in a cytotoxity assay of autologous stimulated CD8+ T cells and target cells from patients Pt.1, Pt.2, Pt.3, Pt.4 (at a ratio 3:1). Different concentrations of Nivolumab were incubated for 24 h together with IgG isotype control or anti-HLA-I antibodies blocking MHC-I (at 1 µg/mL) and the percent of cell lysis was determined by CytoTox-Fluor™. (C) Cytotoxicity inhibition assay evaluating TCR/HLA-I engagement. Stimulated CD8+ T cells incubated with autologous patient tumor cells positive for allele HLA-A24* in the presence of Nivolumab or indicated monoclonal antibody. Values for percentage of specific lysis were calculated as follows: % specific lysis = (test sample value) − (spontaneous release value)(maximum release value) − (spontaneous release value) × 100% specific lysis = (test sample value). Results reported the mean of three independent experiments ± SD. *** p < 0.001.