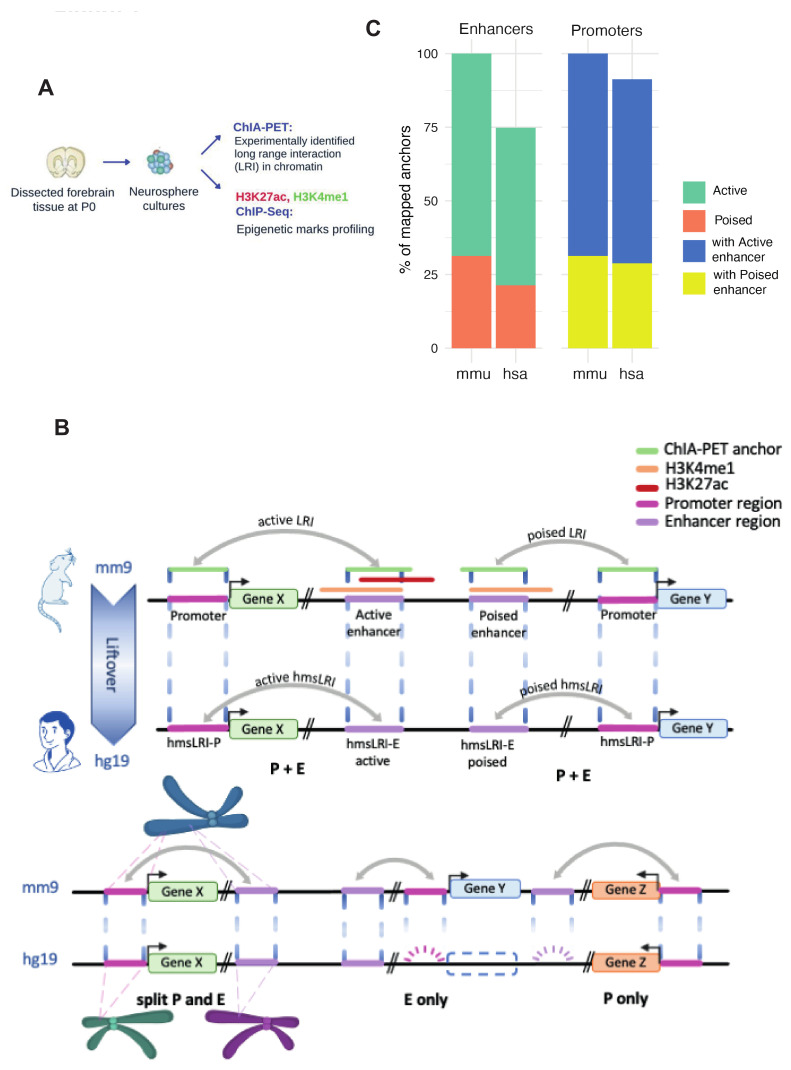
Figure 1.
Identification of human DNA regions syntenic with mouse enhancer–promoter long-range interactions (LRI). (A) Long-range interactions (LRI) identified by RNApolII ChIA-PET in neural stem cells (NSC) cultured in vitro from mouse neonatal forebrain, and regions carrying H3K4me1 and H3K27Ac histone modifications marks as identified by ChIP-Seq were obtained from (Bertolini et al., 2019) [10] (B) Graphical representation of the syntenic mapping between mouse (mm9) and human (hg19) reference genomes. Mouse LRI “anchors” that have syntenic correspondences in the human genome are indicated as hmsLRI-P (promoter) or hmsLRI-E (enhancer). (C) The percentages of mouse promoter and enhancer anchors that “lifted over” to the human genome (imposing a 50% minimal overlap, see Methods).