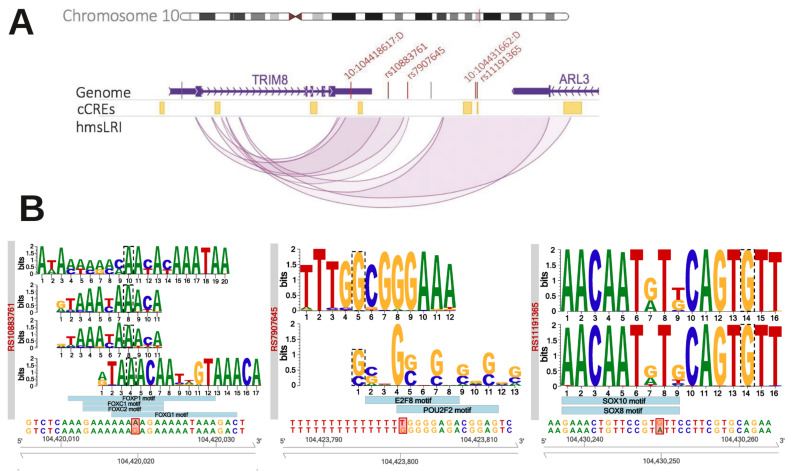
Figure 5.
(A) GWAS-identified risk variants associated with schizophrenia overlap with five different hmsLRI-E connected with theTRIM8gene. Visualization of the human TRIM8-ARL3 locus, located on 10q24.32. In the middle track, in yellow, cCREs identified by (Li et al., 2021) [11] lifted over to the human genome. In the lower track, our hmsLRI: enhancers are represented in their full length, while promoter as their middle point. In the top genome track, vertical bars represent SNPs associated to schizophrenia according to (Li et al., 2021) [11]; the ones shown in red fall into one of our hmsLRI-E connected to the TRIM8 promoter. (B) Neural TF binding site alteration by the risk variants. Alteration by the risk variants of putative neural TF binding sites, as predicted by motifbreakR (Coetzee et al., 2015) [22]. From below upwards: reference DNA sequence and SNP alteration, highlighted in red; light blue boxes represent motifs of transcription factors whose binding is predicted to be strongly influenced by the SNP; detail of the binding motif, retrieved from ENCODE. The motif nucleotide affected by the SNP is surrounded by a dotted line; if the nucleotide is the same as the reference genome, the binding site is predicted to be lost, otherwise it is gained: rs10883761 and rs1191365 disrupt potential binding sites of the TF represented, while rs7907645 leads to the acquisition of the indicated potential novel TF binding sites.