Figure 5. Rescue of respiratory instability in a mouse model of Rett syndrome.
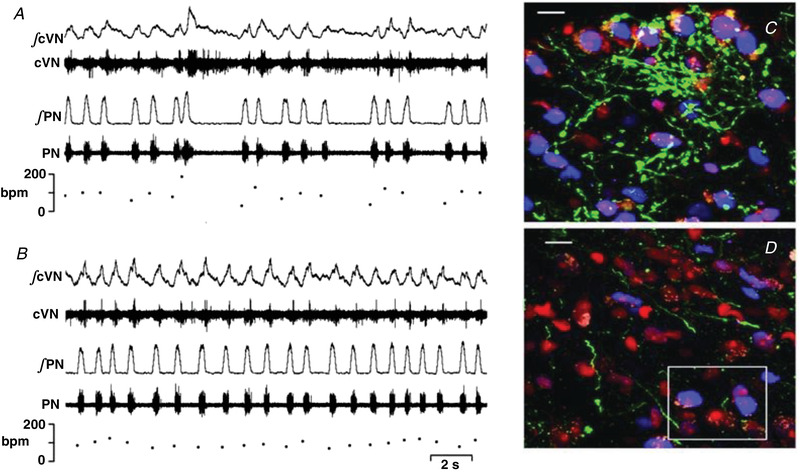
Original recordings of central vagus nerve (cVN), phrenic nerve (PN) and respiratory rate (breaths per minute, bpm) in a Mecp2+/− female mouse before (A) and after (B) microinjection of NO‐711 (a GABA reuptake blocker, 10 μM, 60 nl) into the Kölliker–Fuse pontine nucleus. Note that the apnoeas are associated with prolonged post‐inspiration as seen in cVN. These data emphasise that reduced synaptic GABAergic inhibition in the pons triggers respiratory instability. C and D, GABAergic neurones expressing eGFP under the control of the GAD67 promoter via a knock‐in transgene (green); perikarya are labelled in red (Nissl stain) and MECP2 protein immuno‐reactive (MECP2ir) nuclei are pseudo‐coloured in blue within the Kölliker–Fuse nucleus. C is from a Mecp2+/+/GAD67‐eGFP female and D from a Mecp2+/−/GAD67‐eGFP littermate female. Note the marked reduction in GABAergic projections in the MECP2 deficient female mouse. Scale bars, 10 μm. Data from Abdala et al. (2016).
