Figure 2.
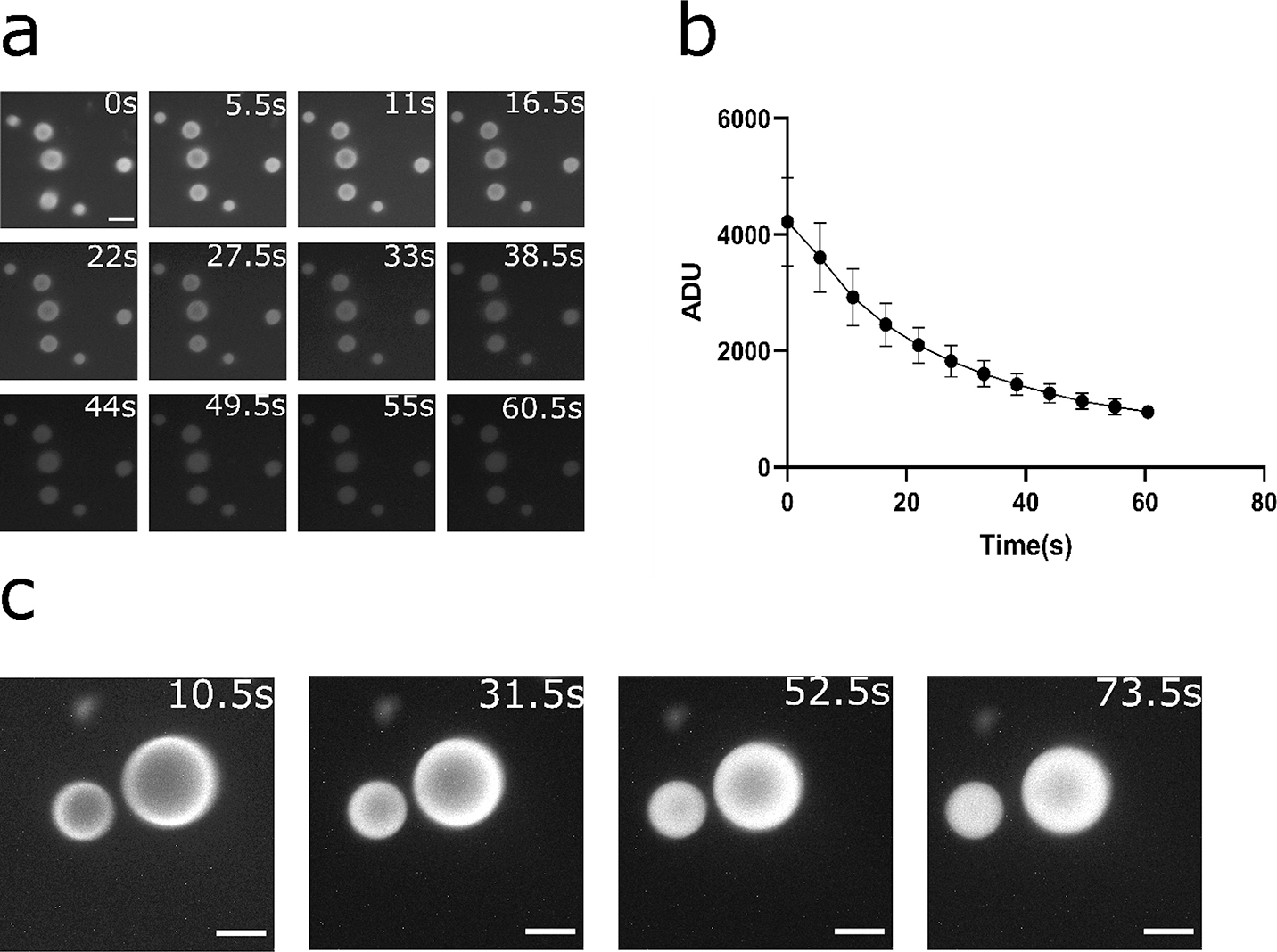
Rapid turnover of substrates and diffusion-limited behavior in the RGG protein coacervates containing NanoLuc. (a-b) Kinetics of bioluminescence from the coacervates for 6μM RGG-NanoLuc-RGG, with substrate concentration of ~833 μM (6x dilution of Nano-Glo assay substrate). (a) Bioluminescence images at different time points. Contrast at default for comparison between time points. Scale bar: 10 μm. (b) Plot of mean pixel intensity inside coacervates over time. Exposure: 5 s. Substrate: 10 μl (~833 μM). Data presented as mean ± SD. (c) Bioluminescence images of RGG-NanoLuc-RGG coacervates over time indicating evidence of diffusion-limited reaction. Reaction was initially predominantly occurring at the coacervate-water interface and gradually reached inside corresponding to substrate diffusion into the coacervates. 20 μl substrate (~1430 μM final substrate concentration) was added into a mixture of 2.25 μM RGG-NanoLuc-RGG with 13.5 μM RGG-RGG. Exposure: 10 s. Scale bars: 10 μm.
