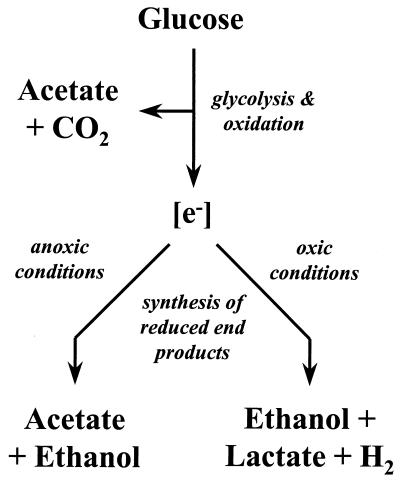
FIG. 5.
Hypothetical scheme illustrating how oxic conditions cause a shift in the flow of reductant ([e−]) by RD-1. The acetate formed under oxic conditions is derived from the oxidation of glucose (upper portion of scheme) rather than reductive synthesis from CO2 via the acetyl-CoA pathway (depicted as the acetate that is produced as a reduced end product under anoxic conditions (lower left branch of figure).