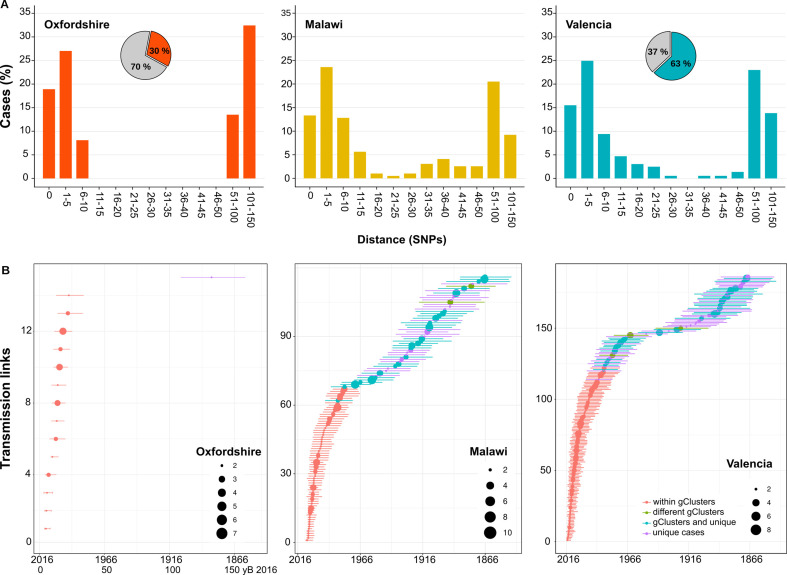
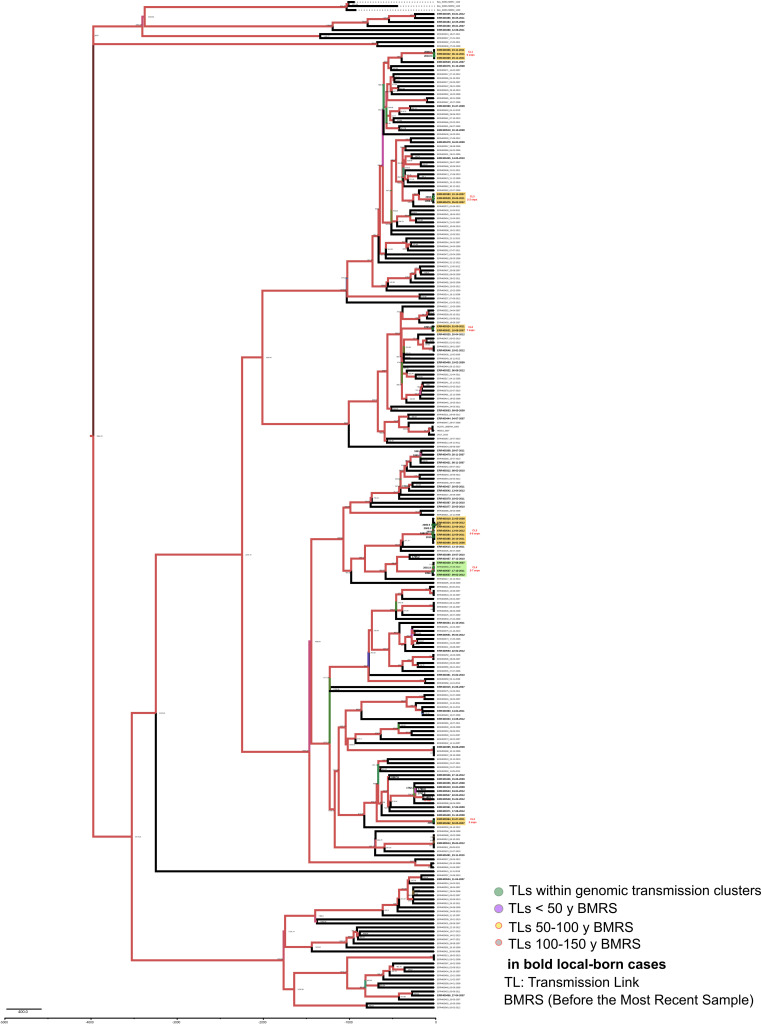
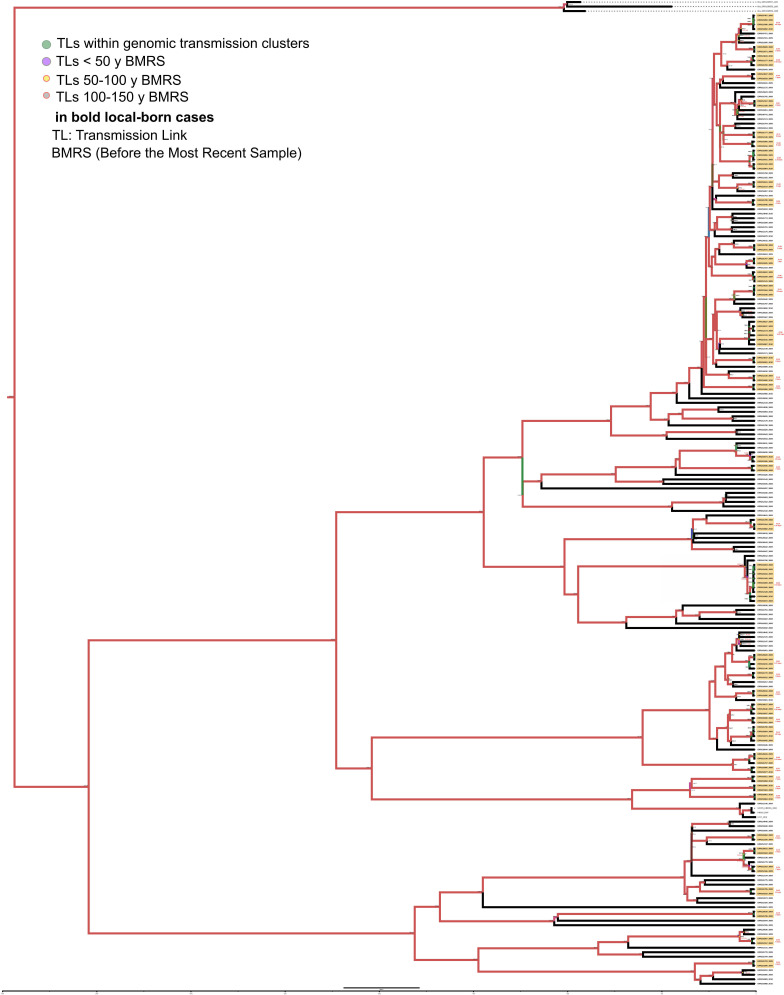
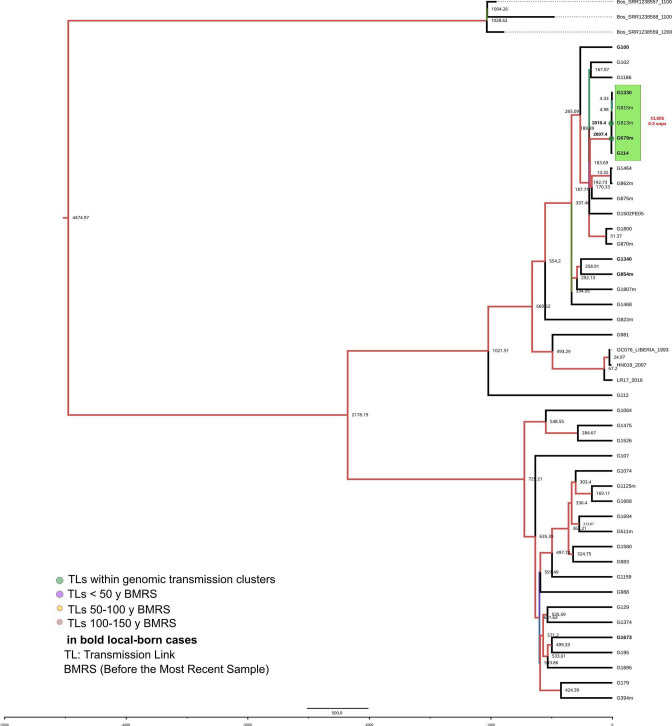
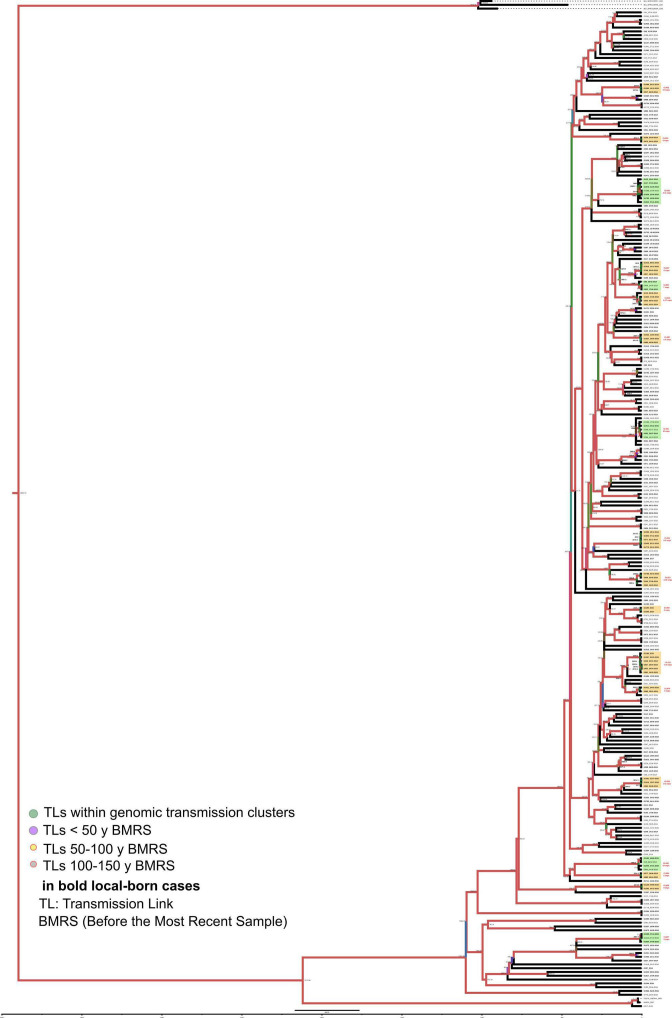
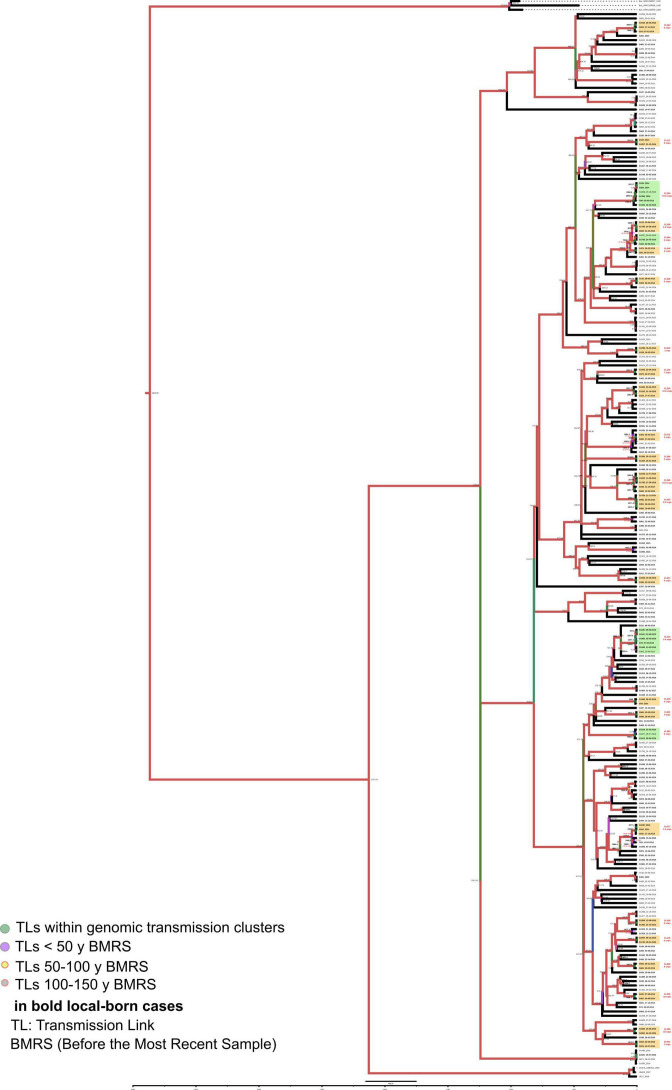
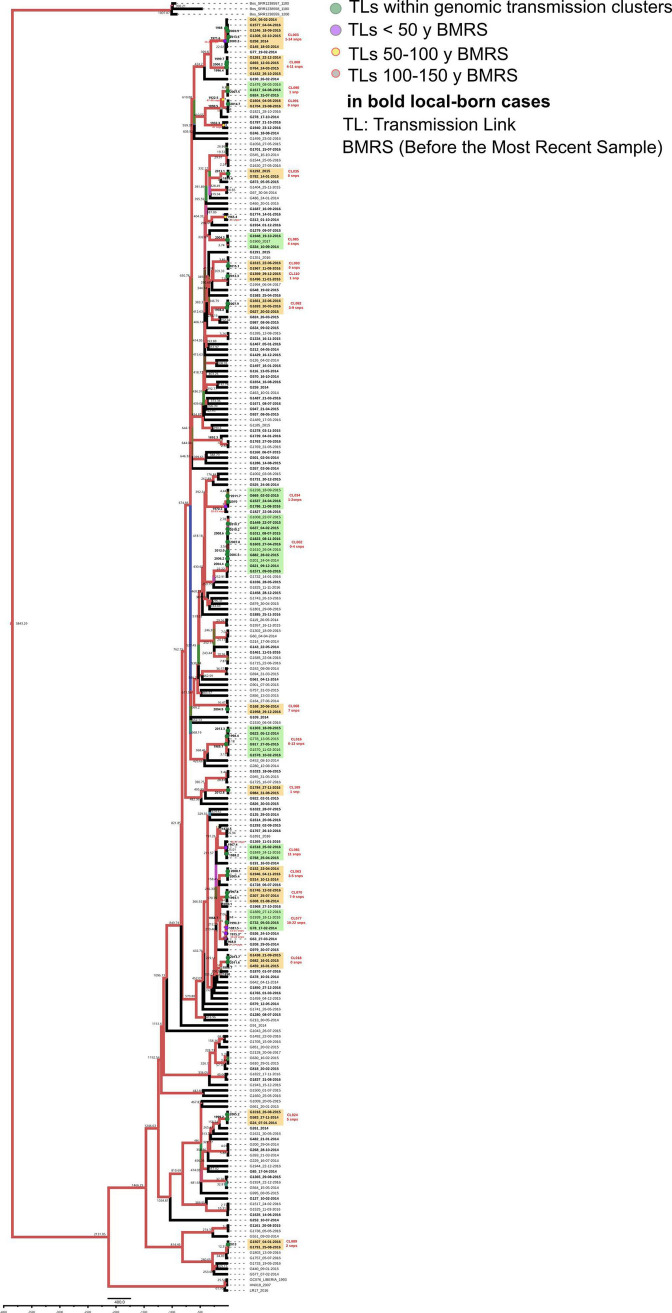
Figure 3. Historical transmission dynamics analysis.
(A) Distribution of local-born cases clustered by different pairwise distance SNP thresholds. Cases are expressed as the percentage of the plotted samples. Pie charts represent the proportion of local-born (color) and foreign-born (gray) cases in each dataset. (B) Age of local transmission links over time in each setting. Circles represent median time, and lines represent 95% high probability density for each transmission link counted. Circle size represents the number of samples included in the corresponding link. Red denotes those transmission links including only samples within the same genomic transmission clusters (gClusters), green denotes links involving samples from different gClusters, blue denotes samples within gClusters and unique, and purple denotes unique cases. All links were obtained from Figure 3—figure supplements 1–6 and are summarized in Figure 3—source data 1–6.