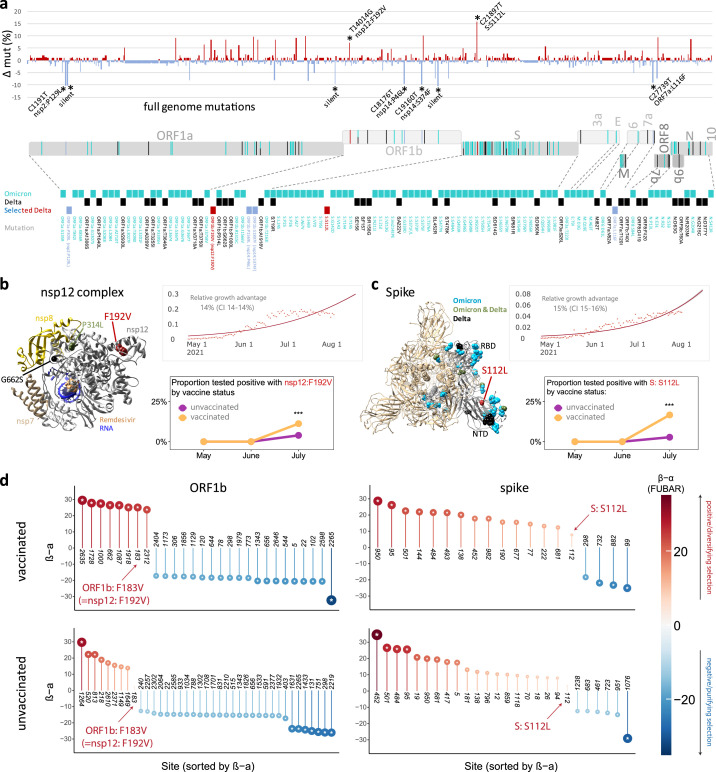
Figure 4.
Full genome mutation analysis, relative growth, and adaptive evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Delta vaccine breakthrough sequences and associated mutations compared to Delta unvaccinated controls.
a, Site-specific base pair mutation frequencies in full genomes (bp 202-29666) of 101 Delta vaccine breakthrough sequences compared to 139 Delta unvaccinated controls from the same cohort. The Wuhan-Hu-1 sequence served as reference. The mirror plot displays differences of mutation frequencies per site between vaccinated and unvaccinated groups, shown along the x-axis (n=791); red (facing up) and blue bars (facing down) refer to elevated mutation rates in vaccinated or unvaccinated individuals, respectively. Significantly enriched mutations in Fisher exact tests are indicated by asterisks (* P<0.05) and are labelled. SARS-CoV-2 coding genomic regions are shown below the plot. Non-synonymous mutations in Omicron (cyan; including B.1.1.529, BA.1, and BA.2 mutations), Delta (black), or Delta breakthrough-enriched mutations (red and blue) are shown by colored ticks. The mutation sites/names are indicated below. b, c, Structural analysis of Delta breakthrough-enriched mutations in comparison to Omicron- and Delta-defining mutations (briefly labelled as Omicron, Delta, or Omicron & Delta, the latter common in both variants). Structures are shown for the nsp12 complex (b) with bound nsp7, nsp8, template-primer RNA, and remdesivir triphosphate (pdb: 7bv2) and for spike (c) in the activated state with one RBD in the up position (pdb: S_ACE2; mutations only shown in the grey, activated protomer). Upper right: The estimated daily proportion of SARS-CoV-2 sequences with indicated mutation through time in the USA is shown as light red dots. The dark red line is the logistic fit. The provided relative growth estimate with confidence interval (CI) reflects the advantage compared to co-circulating strains if variants spread pre-dominantly by local transmission across demographic groups. Lower right: Probability of the detection of a mutation by month in vaccinated (n=132) and unvaccinated (n=283) individuals, adjusted for month of test, sex, and age of participants. *** P<0.001 in a chi-squared test. d, Adaptive evolution analysis of individual sites of a coding gene using a fast, unconstrained Bayesian approximation for inferring selection (FUBAR, Datamonkey), done for vaccinated (n=132) and unvaccinated (n=283) cases. Sites of interest (labelled) are studied in comparison to all sites with significant positive (red, facing up) and negative (blue, facing down) selection per gene. Posterior probabilities >0.9 are considered significant and are indicated by an asterisk inside the circles.
α: mean posterior synonymous mutation rate at a site; β: mean posterior non-synonymous mutation rate at a site; 3a: ORF3a; 7a: ORF7a; 7b: ORF7b; 9b: ORF9b; 10: ORF10; bp: base pairs; E: envelope; mut: mutation; nsp: non-structural protein; N: nucleocapsid; NTD: N-terminal domain; ORF: open reading frame; RBD: receptor-binding domain; S: spike.