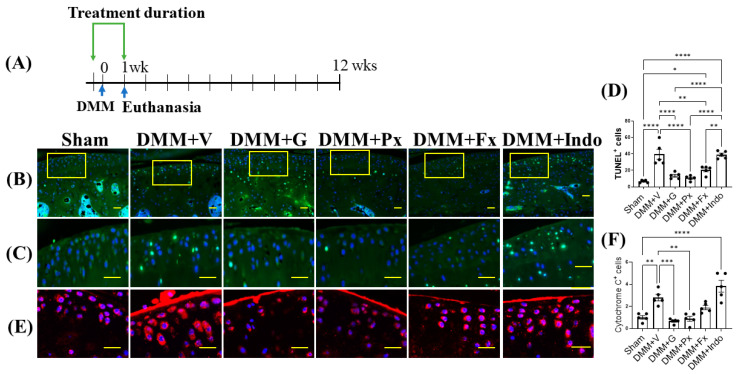
Figure 2.
Early continuous Gβγ-GRK2 inhibition reduces chondrocyte apoptosis and cytochrome C expression in mouse early PTOA cartilage. (A) Schematic representation of timeline of drug treatment after sham (n = 5) or DMM surgeries. Two days before surgery, mice started receiving daily intraperitoneal injections of vehicle (V; n = 10), gallein (G; 10 mg/kg per day, n = 10), paroxetine (Px; 5 mg/kg per day, n = 7), fluoxetine (Fx; 5 mg/kg per day, n = 9), or indomethacin (Indo; 2.5 mg/kg per day, n = 9). All mice were euthanized 1 week after surgery. Green arrows denote the duration of drug treatment. Representative images showing fluorescent staining in the anterior femoral synovium: (B) TUNEL staining of apoptotic cells; scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Magnified images of regions marked by yellow boxes in (B); scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells. (E) IF staining of cytochrome C (red); scale bar, 10 µm. (F) Quantification of the percentage of cytochrome-C-positive cells. DAPI (blue) stains nuclei. n = 5 per group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 in 1 week treatment groups using one-way ANOVA. Values are expressed as means ± SEM.