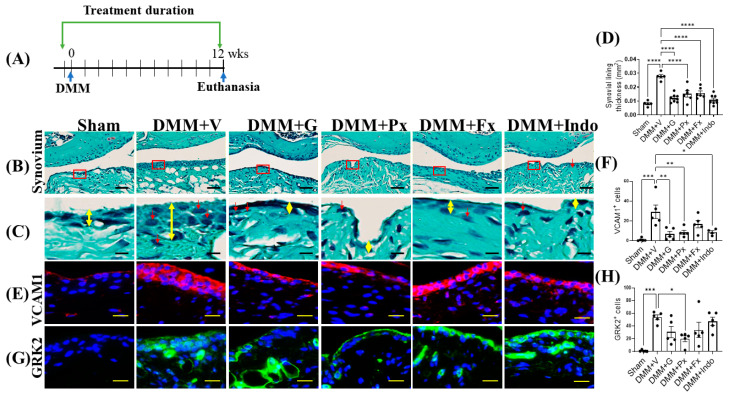
Figure 4.
Early continuous Gβγ-GRK2 inhibition attenuates synovitis in late-stage PTOA. (A) Schematic representation of timeline of drug treatment after sham (n = 5) or DMM surgeries: Two days before surgery, mice started receiving daily intraperitoneal injections of vehicle (V; n = 5), gallein (G; 10 mg/kg per day, n = 7), paroxetine (Px; 5 mg/kg per day, n = 5), fluoxetine (Fx; 5 mg/kg per day, n = 6), or indomethacin (Indo; 2.5 mg/kg per day, n = 7). All mice were euthanized 12 weeks after surgery. Green arrows denote the duration of drug treatment. (B) Representative images of Safranin-O/Fast Green staining of the anterior femoral synovial region of mouse knee sections 12 weeks after DMM or sham surgery; scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Magnified images of regions indicated in red boxes in (B); scale bar, 10 µm. Yellow double-headed arrows depict synovial lining thickness, and red arrows indicate synovial inflammatory cells. (D) Quantification of anterior femoral synovial membrane thickness. Representative IF staining images in the anterior femoral synovium showing (E) VCAM1 (red) and (G) GRK2 (green). DAPI (blue) stains nuclei; scale bar, 50 µm. Quantification of the percentage of positive cells expressing (F) VCAM1 and (H) GRK2. n = 5 per group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 vs. DMM + V group using one-way ANOVA; values are expressed as means ± SEM.