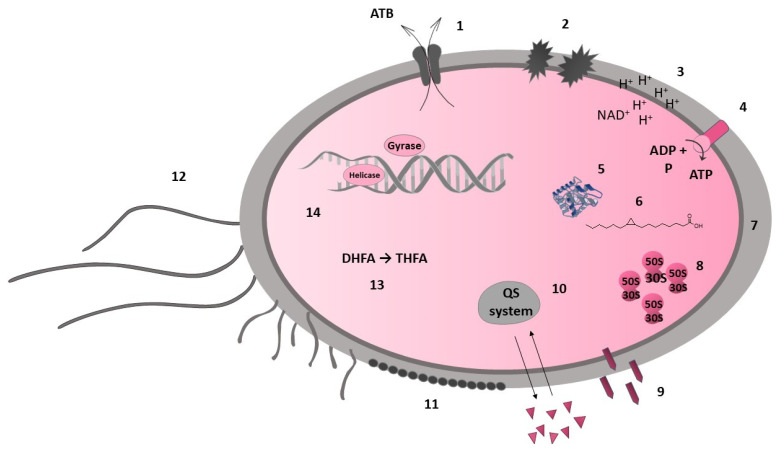
Figure 1.
Bacterial targets of flavonoids. Cell membrane: efflux pump (1), membrane disruption (2), electron transport chain (3), ATP synthesis (4); bacterial metalloenzymes (5); fatty acid synthesis (FabG, FabZ, FabI) (6); cell wall synthesis (7): peptidoglycan, D-alanine–D-alanine ligase; protein synthesis (8): (cell envelope); nonspecific mechanism: bacterial toxic virulence factors (9), quorum sensing system (10), biofilm formation (disruption) (11), motility (12); folic acid metabolism: dihydrofolate reductase (13); nucleic acid synthesis (14): DNA gyrase, topoisomerases I and IV, helicase, DNA intercalation.