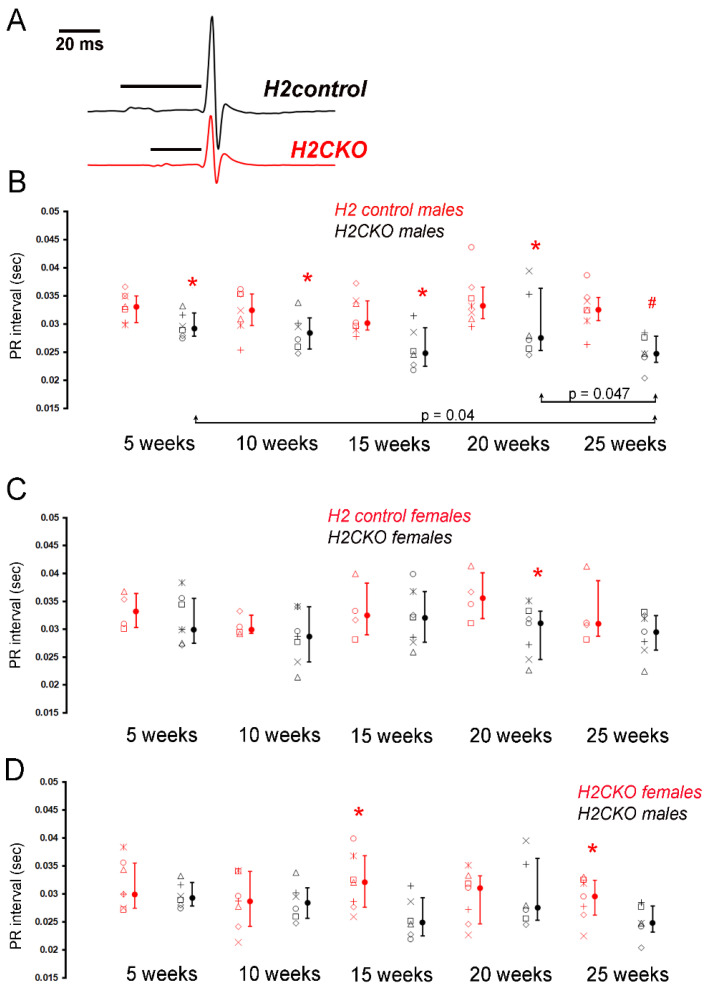
Figure 2.
Loss of Hand2 in post-natal CCS results in sex-dependent effects on AV conduction. (A) Exemplary surface ECGs recorded from an anesthetized H2CKO male (red line) and male H2control littermate (black line) at 25 weeks of age. Horizontal black lines above traces denote lengths of PQ intervals. (B) PR intervals (in seconds) in Lead I ECG analysis from male Cntn2Cre-EGFP/+; Hand2fx/fx (H2CKOs, open black symbols, n = 7) and Hand2fx/fx (H2control, open red symbols, n = 6) mice at 5-week, 10-week, 15-week, 20-week, and 25-week time points. Identical symbols on the left of each line in graph represent the values of the same individual mouse across time points. Filled circles, medians; error bars, 25th and 75th percentiles. * p < 0.05, # p < 0.01 versus male H2control. (C) PR intervals (in seconds) in Lead I ECG analysis from female Cntn2Cre-EGFP/+; Hand2fx/fx (H2CKOs, open black symbols, n = 7) and Hand2fx/fx (H2control, open red symbols, n = 4) mice at 5-week, 10-week, 15-week, 20-week, and 25-week time points. Identical symbols on the left of each line in graph represent the values of the same individual mouse across time points. Filled circles, medians; error bars, 25th and 75th percentiles. * p < 0.05 versus female H2control. (D) PR intervals (in seconds) in Lead I from male (open black symbols) and female (open red symbols) H2CKO mice at 5-week, 10-week, 15-week, 20-week, and 25-week time points. Identical symbols on the left of each line in graph represent the values of the same individual mouse across time points. Filled circles, medians; error bars, 25th and 75th percentiles. * p < 0.05 versus female H2CKO.