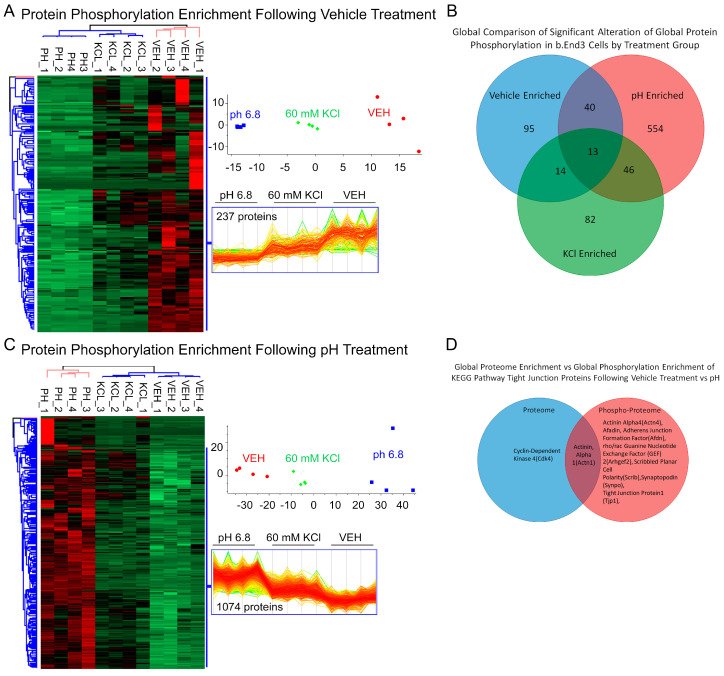
Figure 6.
Global phospho-proteomic analysis of b.End3 endothelial cells following exposure to 60 mM KCl, acidified media buffered to pH = 6.8, and vehicle demonstrates variable phosphorylation enrichment of protein targets unique to each individual treatment, indicative of unique mechanisms of phosphorylation induction identifiable to each individual treatment. (A) Unbiased hierarchal clustering and principal component analysis of the 237 proteins experiencing phosphorylation enrichment following vehicle treatment when compared to KCl and acidified pH treatment, significance assessed by 3-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) analysis of global phospho-proteome data illustrating consistent phosphorylation enrichment between each biological sample (n = 4 per treatment group) clustering into vehicle, 60 mm KCl, and acidified media treatment groups. Heat map visualizes individual protein clustering. (B) Venn diagram comparing total protein phosphorylation enrichment by treatment group; enrichments can be largely identified with a single treatment, small degree of overlap due to large sample pool and ubiquitous nature of peptide phosphorylation. (C) Unbiased hierarchal clustering and principal component analysis of the 1074 proteins undergoing phosphorylation enrichment post exposure to acidified media compared to KCl and vehicle exposure; significance assessed by 3-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) analysis of global phospho-proteome data demonstrating consistent phosphorylation enrichment between biological samples (n = 4 per treatment group) with each protein clustering into vehicle, 60 mM KCl, and acidified media treatment groups. Heat map visualizes clustering of individual proteins. (D) Venn diagram comparing vehicle induced enrichment of total expression and phosphorylation enrichment of tight junction proteins identified in the KEGG pathway bioinformatic database, indicative of tandem alterations to PTM and overall expression of TJ proteins isolated to an individual treatment.