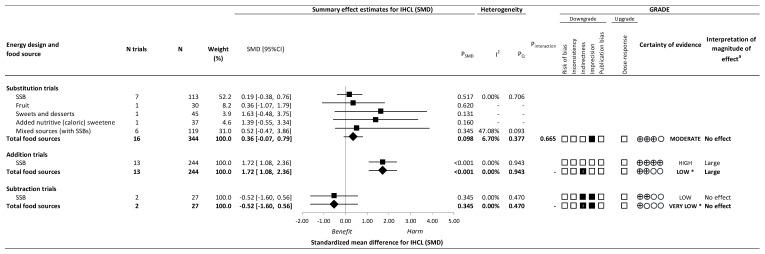
Figure 2.
Summary plot for the effect of important food sources of fructose-containing sugars on intrahepatocellular lipid (IHCL). Data are weighted standardized mean differences (95% confidence intervals) for summary effects of individual food sources and total food sources on IHCL. Analyses conducted by generic, inverse variance random effects models (at least five trials available) or fixed effects models (fewer than five trials available). Between-study heterogeneity was assessed by the Cochrane Q statistic, where PQ < 0.100 is considered statistically significant, and quantified by the I2 statistic, where I2 ≥ 50% is considered evidence of substantial heterogeneity. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) of randomized controlled trials are rated as “High” certainty of evidence and can be downgraded by five domains and upgraded by one domain. The white squares represent no downgrades, while filled black squares indicate a single downgrade or upgrades for each outcome, and the black square with a white “2” indicates a double downgrade for each outcome. CI = confidence interval; GRADE = Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation; IHCL = intrahepatocellular lipid; N = number; SMD = standardized mean difference; SSB = sugar-sweetened beverage. a For the interpretation of the magnitude, we used the MIDs to assess the importance of magnitude of our point estimate using the effect size categories according to new GRADE guidance. * Where there was a significant interaction by food source in substitution and addition trials and SSBs and mixed sources were the sole food sources in subtraction and ad libitum trials, we performed the GRADE analysis for each individual food source. To convert SMD to % liver fat, multiply the SMD by the baseline pooled standard deviation, 0.71%.