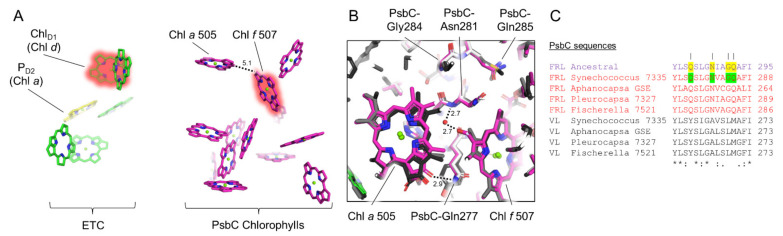
Figure 5.
Conservation of FRL-PsbC interactions near Chl f 507 and Chl a 505. In (A), the Chls and pheophytins in the electron transfer chain and FRL-PsbC of the Synechococcus 7335 apo-FRL-PSII structure are shown as tetrapyrrole rings only from a stromal-side perspective. The Chls d and f are highlighted in red, and Chl a molecules with FRL-specific H-bonds are additionally labeled. In (B), the Synechococcus 7335 apo-FRL-PSII structure (magenta), the homology model of the FRL-PsbC ancestral sequence (white), and two non-FaRLiP holocomplex PSII structures (light and dark grey from T. vulcanus and Synechocystis 6803, respectively) are superimposed. Important H-bonding interactions with distances in units of Å are also shown. In (C), a partial sequence alignment is shown that includes the FRL-PsbC ancestral sequence, and FRL- and VL-specific sequences from extant FaRLiP-capable cyanobacteria. Conserved FRL-specific residues in extant cyanobacteria are highlighted in green in the sequence from Synechococcus 7335. If the same position is conserved in the FRL-PsbC ancestral sequence, it is highlighted in yellow. Vertical lines above residue positions in (C) correspond to amino acids labeled in (B). The Clustal Omega sequence conservation identifiers are shown below the alignment.