Figure 3.
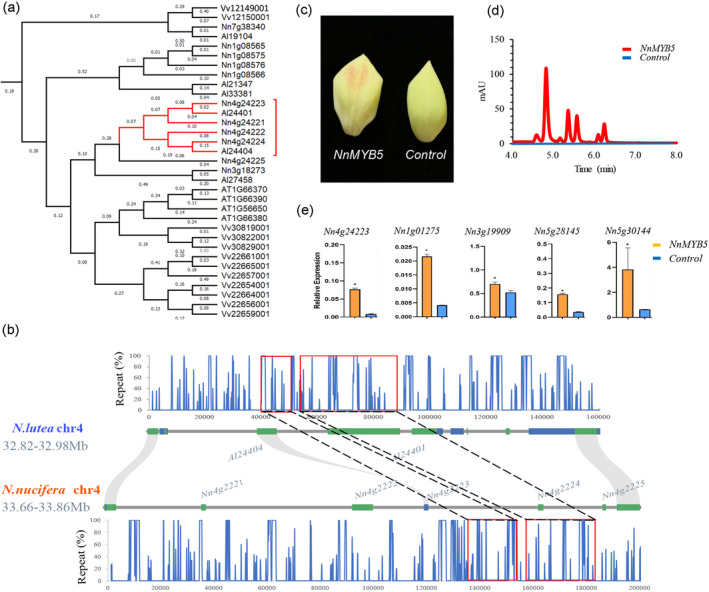
Comparison of pigment pathway regulatory MYB genes in American and Asian lotus. (a) Phylogenetic tree of TT2 clade flavonoid biosynthesis regulatory MYBs. Gene expansions in TT2 clade MYBs detected in Asian lotus, but not in American lotus, are highlight in red. (b) Structural variants between American and Asian lotus in genomic sequences of members (Nn4g24221, Nn4g24222, Nn4g24223, Nn4g24224 and Nn4g24225) of an MYB gene cluster on chromosome 4. The middle panel shows the synteny of NnMYB genomic regions. The upper and lower panels show DNA repeat contents in 1000‐bp windows with 100‐bp steps. Two large structural variants are highlighted in red boxes. The first represents a repeat contraction, whereas the second represents a repeat expansion in American lotus. (c) Transient expression of the NnMYB5 (Nn4g24223) gene in white petals of Asian lotus could induce anthocyanin accumulation. (d) HPLC chromatograph of anthocyanin profile upon transient overexpression of NnMYB5 (Nn4g24223) in lotus petals. (e) Relative expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes upon transient overexpression of NnMYB5 in lotus petals. Increased relative transcript expression of NnANS (Nn1g01275), NnCHS (Nn3g19909), NnF3H (Nn5g28145) and NnFLS (Nn5g30144) was detected in petals transiently overexpressing NnMYB5. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
