Figure 3.
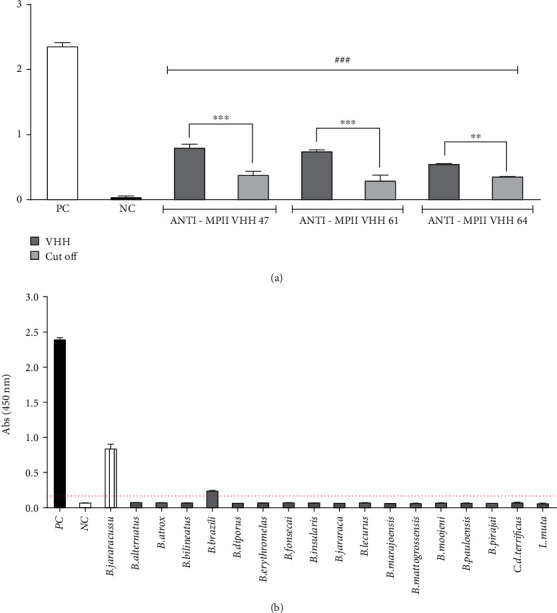
Evaluation of anti-BjussuMP-II VHHs' immunoreactivity by ELISA assay. (a): Absorbances obtained in ELISA performed on plates sensitized with 10 μg/mL of BjussuMP-II and anti-MP-II VHHs in blocking solution (10 μg/mL). PC: positive control with serum from the immunized animal. NC: uncorrelated VHH negative control (anti-Hanta 36 VHH). Columns marked with an asterisk (∗) represent statistical difference in relation to the sample cut-off (∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Columns marked with hash (#) represent statistical difference between the nanobodies and the negative control (###p < 0.001). (b) Absorbances obtained in an ELISA assay performed on a plate sensitized with 1 μg/well of snake venoms of the genera Bothrops, Crotalus, and Lachesis, using a 1 : 1 ratio (p/p) of anti-BjussuMP-II VHH61. The positive control, shown as a striped bar, stands out above the average cut-off value, represented by a dashed line. The specificity of anti-BjussuMP-II VHH61 for the crude venom of B. jararacussu is observed. PC: positive control that corresponds to the absorbance of wells showing the interaction of anti-BjussuMP-II VHH61 with BjussuMP-II from B. jararacussu. NC: negative control corresponding to the absorbance of wells containing BjussuMP-II with uncorrelated anti-Hanta36 VHH obtained from Lama glama, specific for hantavirus.
