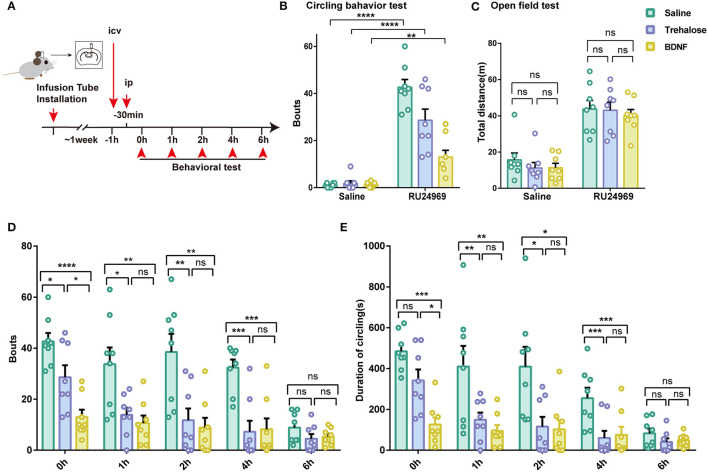
Figure 4.
Increasing the level of BDNF in the brain effectively alleviates stereotypic behaviors. (A) Schematic diagram of icv injection and experimental procedure. (B) RU24969 could still induce obvious circling behavior after icv injection (n = 8 mice; ip saline+ icv saline vs. ip RU24969+icv saline: 1 ± 0.3273 vs. 42.63 ± 3.3, t14 = 12.55, P < 0.0001; ip saline+ icv trehalose vs. ip RU24969+icv trehalose: 1.75 ± 1.082 vs. 28.63 ± 4.698, t14 = 5.575, P < 0.0001; ip saline+ icv BDNF vs. ip RU24969+icv BDNF: 1.125 ± 0.3981 vs. 13 ± 2.885, t14 = 4.078, P < 0.01). (C) icv injection did not inhibit the movement of mice [n = 8 mice; ip saline: F(2, 21) = 0.6426, P = 0.5360 > 0.05; ip RU24969: F(2, 21) = 0.1962, P = 0.8233 > 0.05]. (D,E) Number of bouts and total duration of circling behavior were recorded at different time points after drug administration through the lateral ventricle [n = 8 mice; bouts: 0 h: F(2, 21) = 15.96, P < 0.0001; 1 h: F(2, 21) = 6.184, P < 0.01; 2 h: F(2, 21) = 9.287, P < 0.01; 4 h: F(2, 21) = 13.09, P < 0.001; 6 h: F(2, 21) = 1.749, P = 0.1983 > 0.05. Duration: 0 h: F(2, 21) = 13.52, P < 0.001; 1 h: F(2, 21) = 9.711, P < 0.01; 2 h: F(2, 21) = 6.002, P < 0.01; 4 h: F(2, 21) = 13.25, P < 0.001; 6 h: F(2, 21) = 1.527, P = 0.2402 > 0.05]. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by two-tailed Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparisons with a Bonferroni correction; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns stands for “not significant”.