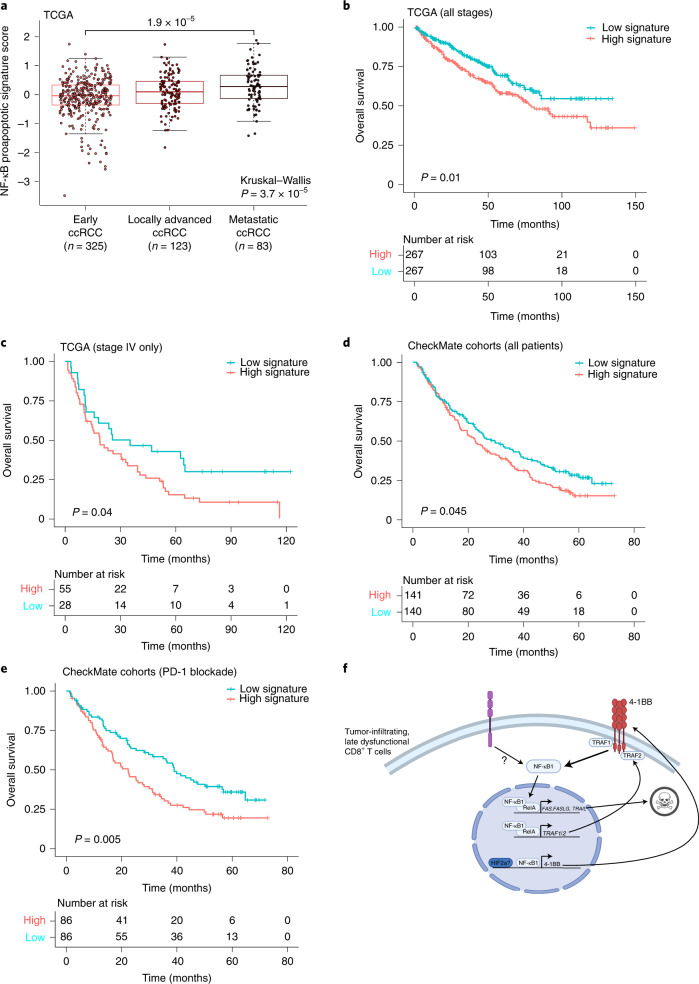
Fig. 5. A chromatin-derived NF-κB signature of late dysfunctional CD8+ T cells predicts patient survival.
a, A gene expression signature of pro-apoptotic NF-κB targets in late dysfunctional CD8+ T cells for the indicated disease stage in the external TCGA KIRC cohort (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test for pairwise comparison; Kruskal–Wallis test for global P value; n = 325 patients for early ccRCC, n = 123 patients for locally advanced ccRCC, n = 83 patients for metastatic ccRCC). Box plot statistical values including whiskers, quartiles, and median, max and min values are listed in the source data. b, Overall survival for the overall TCGA ccRCC cohorts based on high pro-apoptotic NF-κB signature (≥median) versus low signature expression. Log-rank test was used to compare the survival between the two groups. χ2 = 6.6 on 1 degrees of freedom, P = 0.01. c, Overall survival for the advanced TCGA ccRCC cohorts based on high pro-apoptotic NF-κB signature (≥median) versus low signature expression. Log-rank test was used to compare the survival between the two groups. χ2 = 4.3 with 1 degree of freedom, P = 0.04. d, Overall survival for the entire CheckMate cohort, based on high pro-apoptotic NF-κB signature (≥median) versus low signature expression. Log-rank test was used to compare the survival between the two groups. χ2 = 4 with 1 degree of freedom, P = 0.045. e, Overall survival for the PD-1 blockade CheckMate cohort, based on high pro-apoptotic NF-κB signature (≥median) versus low signature expression. Log-rank test was used to compare the survival between the two groups. χ2 = 7.7 for 1 degree of freedom, P = 0.005. f, Model of the NF-κB pro-apoptotic program in late dysfunctional CD8+ T cells. Image created with BioRender.com.