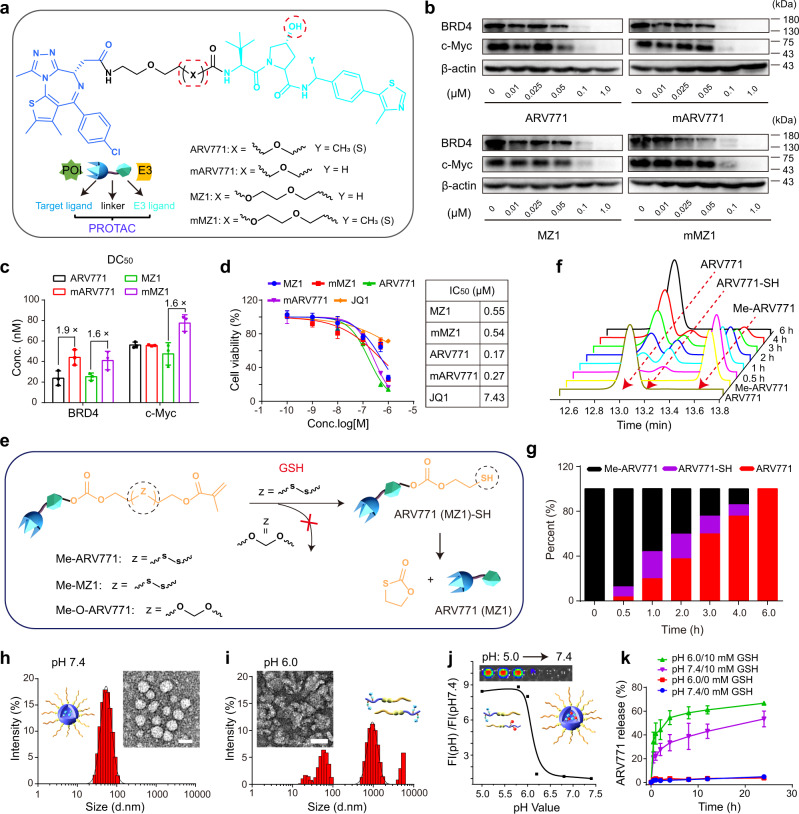
Fig. 2. Synthesis and characterisation of the BRD4 PROTAC and POLY-PROTAC NPs.
a Synthesis of the BRD4-targeted VHL PROTACs. b Western blot assay of PROTAC-mediated BRD4 degradation and c-Myc downregulation in MDA-MB-231 breast tumour cells after 24 h of incubation. c Western blot assay-determined half BRD4 degradation concentration (DC50) values of the PROTACs (n = 3 biologically independent cells). d PROTACs efficiently inhibited the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose-dependent manner in vitro (inset shows the IC50 values of the indicated PROTACs and JQ1). Cells were incubated with the PROTACs or JQ1 for 72 h before being subjected to the CCK-8 assay (n = 4 biologically independent cells). e Schematic illustration of the GSH-triggered activation of ARV771 from Me-ARV771. f HPLC chromatograms of the reduction-mediated ARV771 restoration and g quantitative ARV771 release percentages from reduction-activatable Me-ARV771 via incubation with 5.0 mM DTT. h, i Representative DLS data and TEM images of the PGD7 NPs at h pH 7.4 and i pH 6.0 (scale bar = 50 μm). j Acid-activatable fluorescence profile of PPa-labelled PGDA7 NPs (the fluorescence intensity was normalised to that determined at pH 7.4). Inset shows the fluorescence image of the PGDA7 NP suspensions at different pH values. k GSH-triggered ARV771 release from the PGD7 NPs at pH 7.4 and 6.0 (with or without 10 mM GSH addition) (n = 3 independent experiments). All data are presented as mean ± SD.