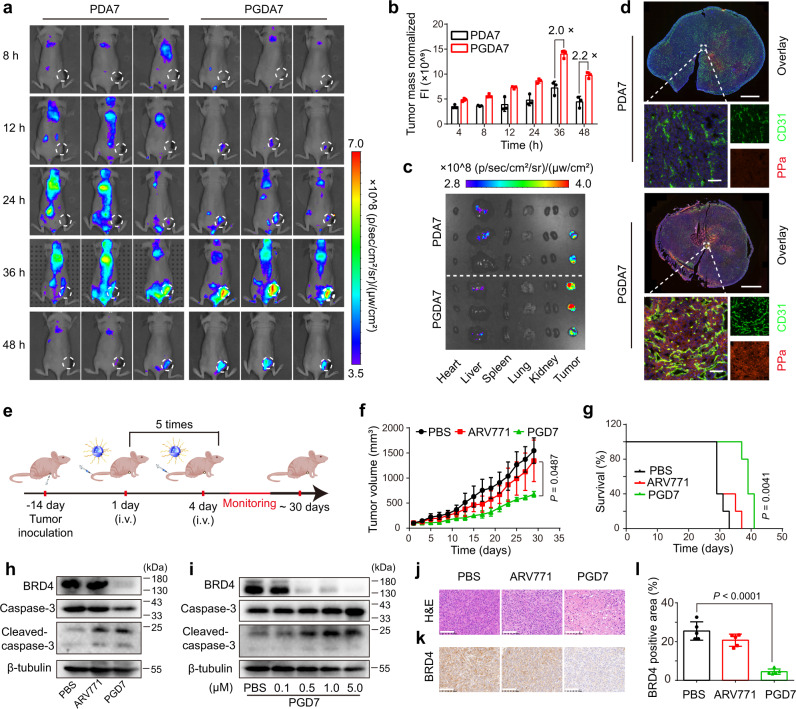
Fig. 4. Stimuli-activatable POLY-PROTAC NPs specifically accumulated at the tumour site and suppressed tumour growth in vivo.
a Fluorescence images of POLY-PROTAC NPs distribution in MDA-MB-231 tumour-bearing nude mice in vivo. MMP-2-activatable PGDA7 NPs specifically accumulated at the tumour site. b Normalised fluorescence intensities of the tumour tissue (n = 3 biologically independent mice). c Ex vivo fluorescence images of the major organs and tumour (the major organs and tumours were harvested 48 h post-injection). d Ex vivo CLSM images of tumour sections at 48 h post-injection (top panel scale bar = 2.0 mm, bottom panel scale bar = 50 μm). e Treatment schedule of the POLY-PROTAC NPs antitumor study in MDA-MB-231 tumour-bearing nude mice. f, g PGD7 NPs efficiently suppressed MDA-MB-231 tumour growth without notable adverse effects. f Tumour growth curves and g survival plots of the tumour-bearing BALB/c nude mice upon POLY-PROTAC NPs treatment (n = 5 biologically independent mice) Statistical analysis of f was performed by two-sided unpaired t-test. Statistical significance of g was calculated by survival curve comparison with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. h, i Western blot assay of PGD7 NP-induced BRD4 degradation and caspase-3 activation in h MDA-MB-231 tumours in vivo (the tumours were harvested on the second day after five cycles of treatment), and i tumour cells in vitro as a function of ARV771 concentration. j H&E staining of the tumour sections at the end of the antitumor study (scale bar = 100 μm). k–l PGD7 NPs degraded the BRD4 protein and activated caspase-3 in vivo. k Immunohistochemical staining of the BRD4 protein (scale bar = 100 μm) and l Semiquantitation of IHC-determined BRD4 expression in the tumour sections (n = 5 biologically independent mice). Statistical analysis was performed by two-sided unpaired t-test. All data are presented as mean ± SD.