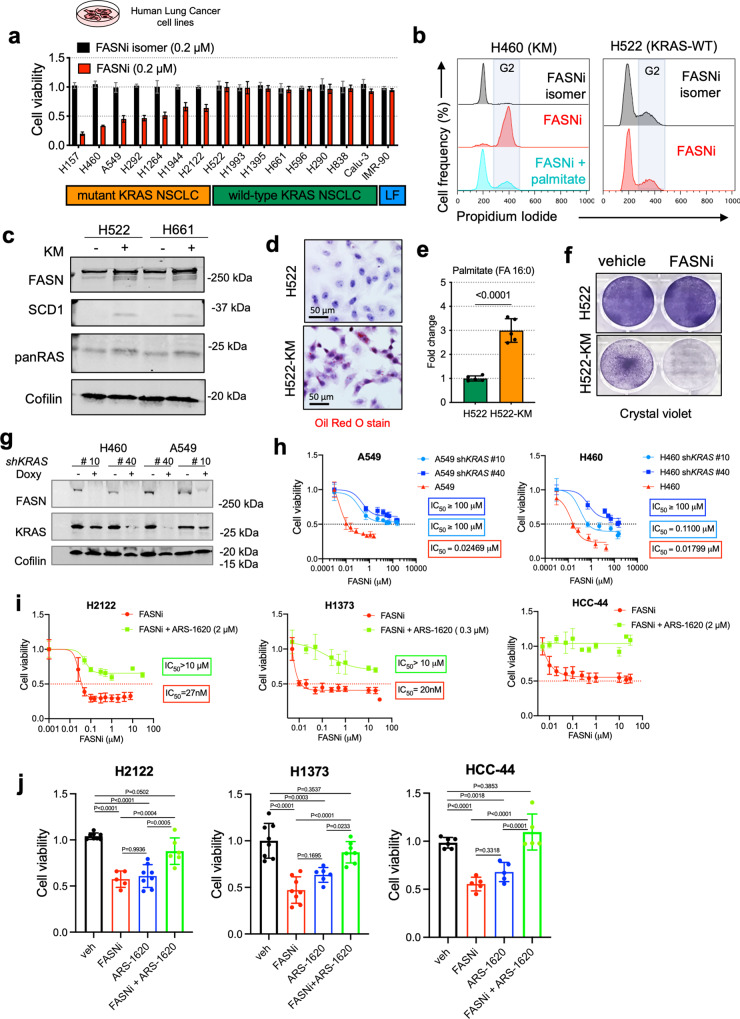
Fig. 2. KM is required to induce dependency on FASN.
a Viability assay of human LC-derived cell lines (n = 2 biological independent experiments). Cell line, genotype and treatments are indicated. LF: lung fibroblasts. b Cell cycle analysis of H460 and H522 cells, as representative examples of KM and KRAS-WT LC cells, treated as indicated. Cell populations indicate singlets in the FL2-W/FL2-A gate. Refer to Supplementary Fig. 11 for a representative gating strategy. c Representative immunoblots of FASN, SCD1 and pan-RAS in H522 and H661 cells transduced as indicated (n = 2 independent experiments). d Oil red O staining, relative steady-state quantification of palmitate (FA 16:0) (e) and crystal violet assay (f) of H522 and H522-KM cells treated as indicated. g Immunoblot of FASN and KRAS in H460 and A549 cells transduced with doxy-inducible shRNAs targeting KRAS. h MTT viability assay of H460 and A549 cells treated with FASNi before and after induction of KRAS knock-down (n = 2 biological independent experiments). i, j MTT viability assays of H2122, H1373, and HCC-44 cells (KRASG12C mutant) treated with FASNi alone or in combination with the KRASG12C inhibitor ARS-1620 (n = 2 biological independent experiments). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. In e Student t-test with. In j one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.