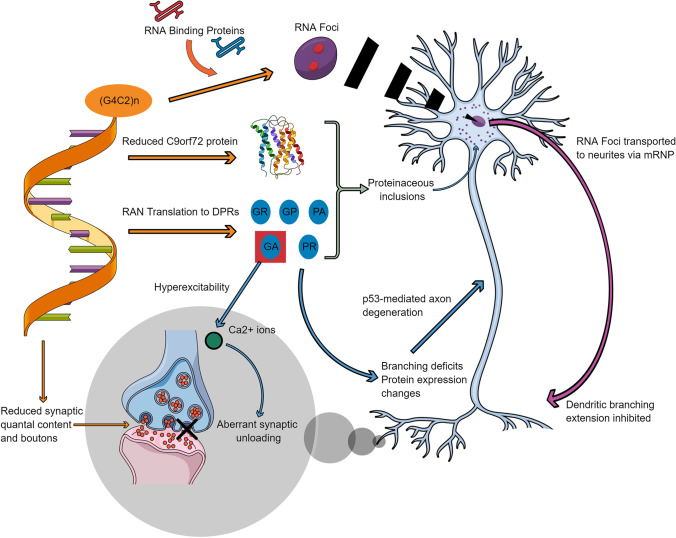
Fig. 1.
Putative mechanisms underlying synaptic dysfunction in C9orf72-ALS/FTD. A schematic detailing the role of the hexanucleotide expansion, (G4C2)n, of the C9orf72 gene in driving synaptic, axonal and dendritic dysfunction. This operates through the three main pathogenic mechanisms implicated in C9-ALS/FTD which are haploinsufficiency of the C9orf72 protein and the accumulation of RNA foci and dipeptide repeats (DPRs). Abbreviations: p53, tumour protein p53; RAN, repeat-associated non-AUG; Ca2+, calcium ions; mRNP, messenger ribonucleoprotein; RNA, ribonucleic acid