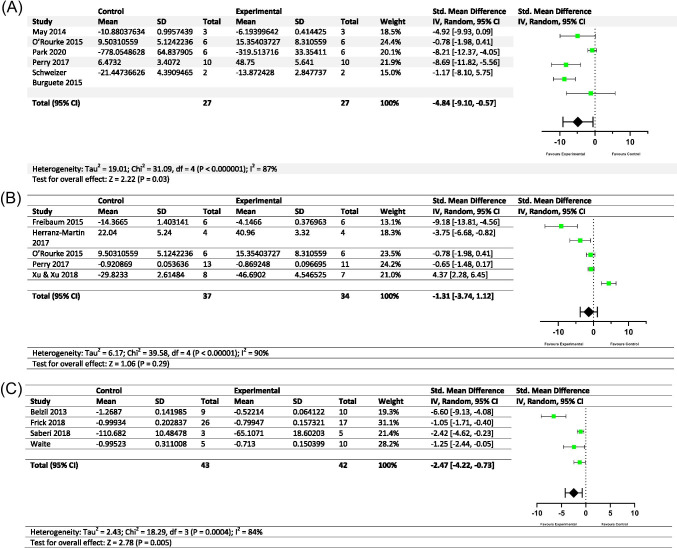
Fig. 4.
Meta-analysis using a random effects model of selected studies relating to synaptic deficits. (A) Shows the meta-analysis for dendritic defects assessing reductions in arborisations such as crossings and branchpoints (P = 0.03). (B) Shows the meta-analysis for neuromuscular junction (NMJs) abnormalities assessing synaptic bouton counts and fractured NMJs (P = 0.29). (C) Shows the meta-analysis for reductions of C9orf72 protein in human patients using frontal cortex and cerebellar samples (P = 0.005). All studies were highly heterogenous (I2 ≥ 84%; P ≤ 0.0004). The figure was generated using the RevMan 5.4 software. Abbreviations: SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval