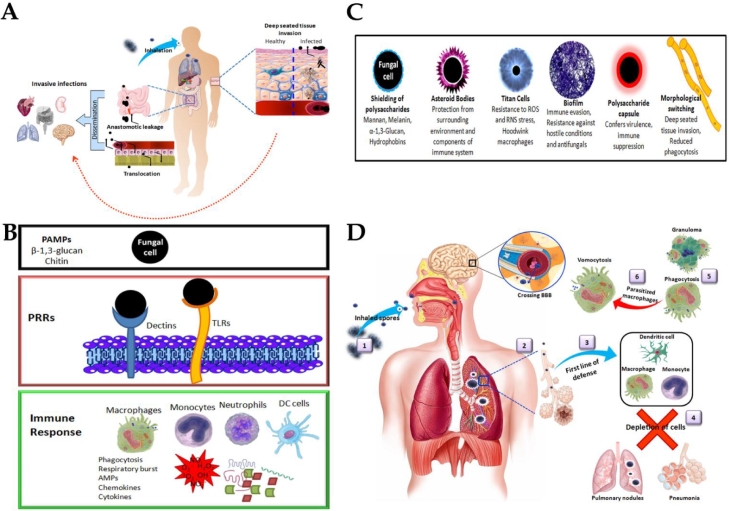
Fig. 2.
A. Routes of invasion of fungal pathogens. B. Pathogen recognition and response in host immune system. C. Morphological modulation of fungal cells for immune evasion. D. Pulmonary transmission and pathogenesis of invasive fungal infections. 1. Inhalation of spores or conidia; 2. Entry into alveoli; 3. Eliciting first line of defense; 4. Depletion of phagocytic cells leads to disease progression as pulmonary nodules and pneumonia; 5. Macrophages phagocytise the fungal cells or encapsulate and form granuloma; 6. Fungal cells parasitize the macrophages that leads to vomocytosis of intact fungi and circulation into bloodstream and crossing blood brain barrier to cause systemic infections.