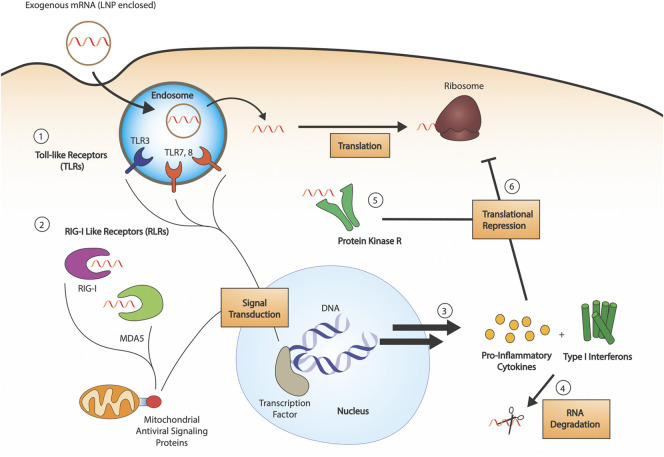
FIGURE 1.
RNA sensing by the innate immune system. 1) RNA sensing Toll-like receptors (TLR3, TLR7, TLR8) are endosomal compartment receptors in sentinel cells, which activate upon late-endosomal acidification. Exogenous RNA is endocytosed by the cell, and pathogen associated molecular patterns are detected by the TLRs (dsRNAs, uridine-rich ribonucleosides, etc.). 2) RIG-I like receptors (RLRs) are cytosolic receptors present in all cell types. Both RIG-I and MDA5 are 5′-triphosphate dependent sensors, with some affinity for both dsRNA and ssRNA. Their activation leads to signal transduction through mitochondrial antiviral signaling proteins. 3) Innate immune detection of exogenous RNA leads to production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I interferons, which activate RNA degradation 4). 5) Protein kinase R (PKR) is a cytosolic sensor also involved in dsRNA sensing, the activation of which leads to phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2α. 6) The combined action of produced cytokines and PKR leads to translational repression.