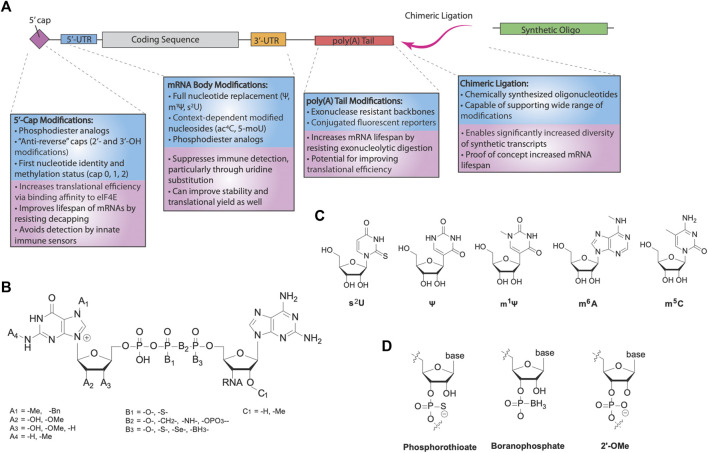
FIGURE 2.
RNA modifications for mRNA therapeutics. (A) Categories of different modifications for mRNA. Modification of the cap and nucleotide substitution of the mRNA body are important for innate immune avoidance. Translational efficiency and mRNA stability are further modulated by various modifications, via increased eIF4E binding and reduced hydrolysis by nucleases. Additionally, chimeric ligation is a separate class of modification enabling incorporation of highly modified synthetic oligonucleotides, forming chimeric mocRNAs. (B) Chemical structure of 5′-caps. Eukaryotic caps are typically modified on the first base (A’s), triphosphate (B’s), or second base (C’s). (C) Common modified bases used for modification of mRNA. 2-thiouridine (s2U), pseudouridine (Ψ), and N1-methylpseudouridine (m1Ψ) are uridine substitutes, whereas N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an adenosine substituent and 5-methylcytosine (m5C) is a cytosine substituent. (D) Common backbone modifications used for modification of mRNA. The phosphate backbone and 2′-OH are frequently modified.