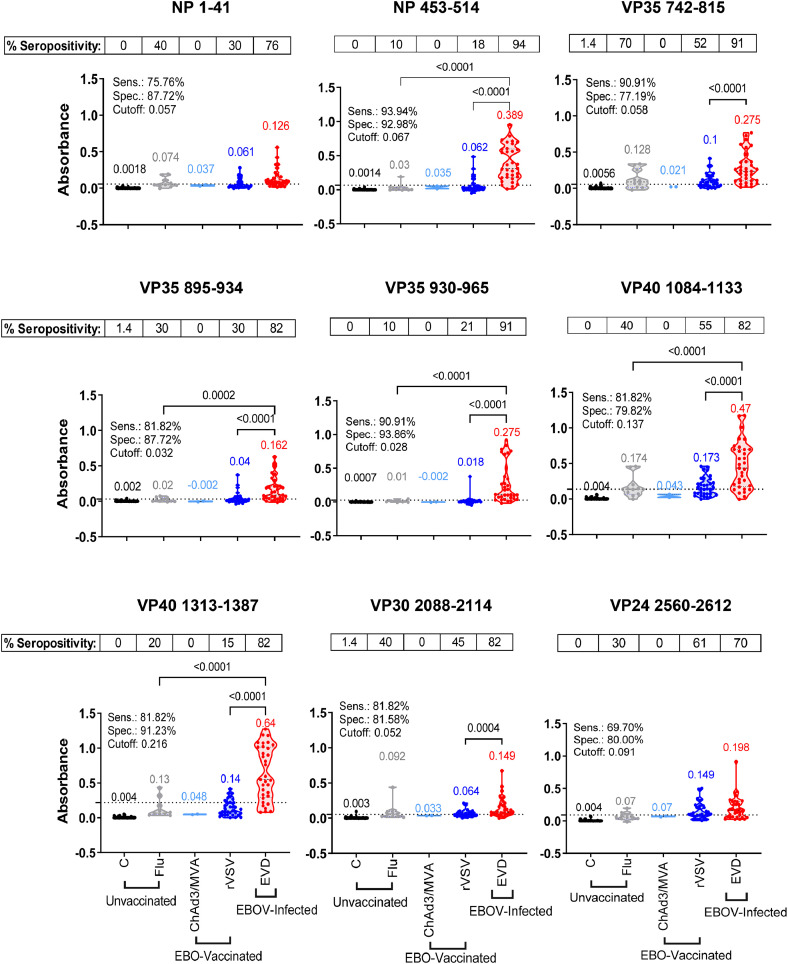
Figure 2.
Reactivity of human samples to individual EBOV peptides in ELISA. IgG absorbance values at a 1:100 serum/plasma dilution for each sample group namely, unvaccinated [healthy controls (C, black, n = 69) and H1N1-infected (Flu, grey, n = 44)], EBO-vaccinated [ChAd3/MVA-vaccinated (ChAd3/MVA, light blue, n = 2) and rVSV-ZEBOV (ERVEBO) vaccinated (rVSV, blue, n = 33)], and EBOV-infected convalescent sera from EVD survivors (EVD, red, n = 33) were plotted based on the reactivity to each 9 individual peptides. Mean absorbance values for each group are color-coded and indicated above each group. Cut-off value for each individual peptide was determined separately by ROC curve analysis and represented as a dotted line on the Y-axis. Specimens with an absorbance greater than Cut-off value are considered EBOV seropositive and those with absorbance less than Cut-off value are considered EBOV seronegative. Percent seropositive are shown for each sample cohort above the panel. Area under the ROC curve was performed to calculate sensitivity (%) and specificity (%) values with 95% CI (confidence interval) by comparing ELISA reactivity for 33 EVD survivors vs. 148 uninfected samples. Statistical differences among groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey-adjusted p values using a pairwise multiple comparison. Statistically significant differences between cohorts are shown. All ELISA experiments were performed twice and the researcher performing the assay was blinded to sample identity. The variation for each sample in duplicate ELISA runs was <7%. The data shown are the average value of two experimental runs. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)