Figure 2. Conservation of the Spo0A receiver domains in B. subtilis and C. difficile.
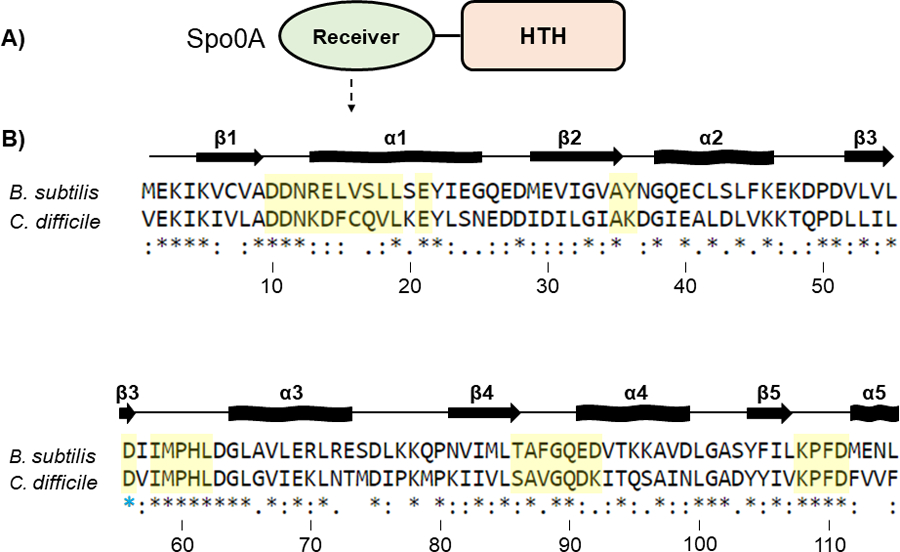
A) Graphic representation of Spo0A domain structure. Functional residues responsible for protein - protein interaction and Spo0A activation are located in the N-terminal receiver domain. The C-terminal region of Spo0A is defined by a helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA-binding domain. B) Amino acid sequences of the Spo0A receiver domains for B. subtilis str. 168 (BSU_24220, top) and C. difficile 630 (CD630_12140, bottom). Residues important for activity that were chosen for mutation in C. difficile are highlighted in yellow. The blue star (*) is the conserved site of phosphorylation. Alignment performed using Clustal Omega. Arrows represent beta sheets, and waved rectangles represent alpha helices.
